Group Mentality
Near a second-order phase transition, fluctuations occur on all length and time scales—no matter how much you zoom in on the system, fluctuations look the same. This “scale invariance” has been observed in bird flocks, and, as reported in Physical Review Letters, bacteria. Xiao Chen at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China, and colleagues argue that similarities in the collective motion of birds and bacteria, organisms separated by one million times in size, may suggest a fundamental principle at work.
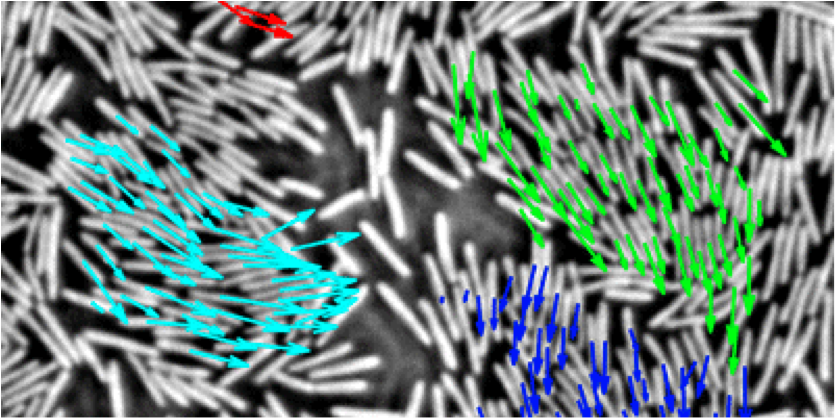
With a camera mounted on a microscope, Chen et al. took a series of photos of an expanding colony of rod-shaped bacteria, labeling the position, orientation, and velocity of the roughly cells in each image. Bacteria tend to form clusters: blobs of bacteria in which every cell is within a certain distance and angular deviation from its neighbor. Chen et al. find that the correlation lengths for fluctuations in speed or orientation within a cluster are always of the size of the cluster itself—in other words, scale invariant.
Researchers have suggested that scale-free correlations in bird flocks offer greater protection, since one bird’s response to a threat can be transmitted to the flock as a whole. Unlike birds, though, which tend to move in a single flock and fly in all directions, bacteria move between clusters and are typically confined to a surface, so Chen et al. are cautious in interpreting their findings. – Jessica Thomas