Radiation-Belt Scattering in the Lab
The flux of electrons in Earth’s radiation belts can sometimes vary by a factor of in a matter of hours. Space scientists assume that these rapid changes are partly due to the scattering of electrons from so-called whistler-mode waves—plasma waves in the Earth’s magnetosphere with frequencies in the kilohertz range. A first experimental observation of this scattering process, recreated in the lab, is presented in Physical Review Letters.
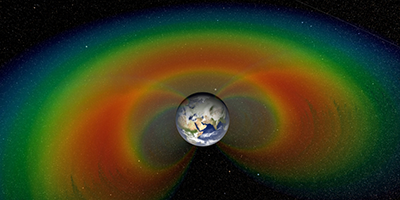
The Van Allen radiation belts are two donut-shaped regions, in which charged particles spiral along the Earth’s magnetic field lines. The outer belt can vary dramatically, especially during geomagnetic storms. One possible factor contributing to this variation is the resonant interaction of electrons with whistler modes whose frequency matches the electrons’ gyrofrequency. However, verifying this hypothesis has been difficult because the change in the electron trajectory is very small in a laboratory experiment.
Bart Van Compernolle and his colleagues at UCLA have managed to observe electron scattering from whistler waves for the first time. Inside the Large Plasma Device (LAPD) at UCLA, they generated a beam of -kilo-electron-volt electrons, which spiraled along the machine’s magnetic field lines before reaching a detector with a small pin-hole entrance. This hole filtered the incoming electrons depending on the pitch angle of their helical trajectory. The team then induced whistler waves in the LAPD plasma with a radio antenna and observed a drop in the number of electrons making it to the detector. The drop was consistent with the expected change in pitch angle from scattering off of whistler waves. The authors expect this verification should help interpret data coming from satellites, such as the recently launched Van Allen Probes that are studying the Earth’s radiation environment. – Michael Schirber