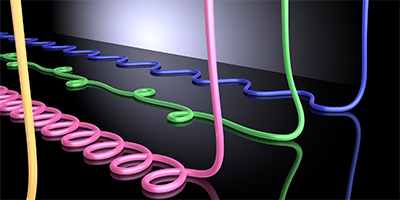
Coiling Viscous Jets
When poured onto toasted bread, honey can deposit in a variety of wavy patterns, like meanders, loops, or coils. Similar coiling patterns are seen in a variety of systems, ranging from jets for 3D printing to underwater optical fibers. But, to date, no theoretical models have been able to explain the complex features observed in experiments. Now, a team led by Pierre-Thomas Brun at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, has formulated a theory that can predict the patterns created when a viscous fluid falls onto a surface.
The authors modeled a thin thread of fluid landing onto a moving belt—a setup known as a fluid-mechanical sewing machine. They show that the system can be described by equations that depend on only a few “state” variables, such as the position where the jet hits the belt and the angle of the thread at that contact point. Like the thermodynamic state variables of a gas (temperature, pressure, or volume), these variables determine the present state of the system, as well as its future behavior. Depending on parameters like the height from which the fluid falls or the belt speed, the theory predicts that the system enters different phases, each of which corresponds to the formation of a specific configuration of loops and coils or, above a critical belt velocity, a straight line. The model successfully reproduces features observed in previously reported experiments. According to the authors, the theory could also be applicable to thin solid threads and might help guide the fabrication of patterned microstructures made of fiber or fabric.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Matteo Rini