Hunting Grounds for Dirac Electrons
Electrons in graphene—a two-dimensional (2D) form of carbon—behave a lot like massless particles. The phenomenon is at the heart of why graphene’s electrons have such a high mobility. According to theoretical calculations, similar behavior, and new effects, might be observed in 2D materials with crystal structures that share little likeness to graphene’s honeycomb lattice.
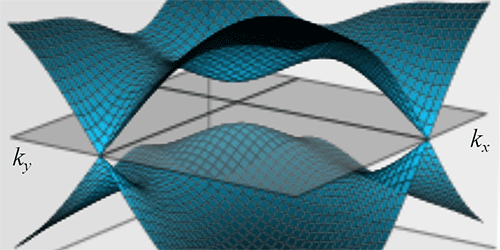
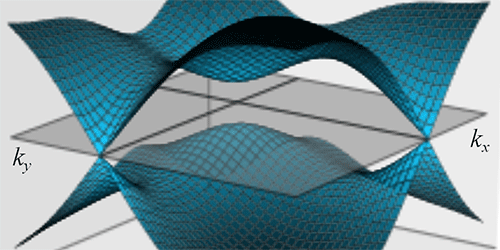
Graphene’s unusual electronic properties stem from its crystal structure, which gives rise to cone-shaped electronic energy bands that touch at points. Electrons that fill the bands near these points can be characterized by the same Dirac equation that describes photons and other relativistic particles traveling in 2D. This description isn’t perfect, however, because the bands near such “Dirac points” are distorted by the spin-orbit effect, an interaction between the spin and momentum of graphene’s electrons.
Using spatial-symmetry arguments, Steve Young of the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington DC and Charles Kane of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, identified a family of 2D crystalline semimetals with Dirac points that are immune to the spin-orbit effect. This immunity gives some tunability to the materials that isn’t available in graphene. Specifically, the authors show that breaking certain symmetries in the structures—say, by distorting the crystal lattice—can transform the metals into either a normal insulator or a topological insulator, a material whose surface electrons can travel without backscattering. In addition to fundamental interest, topological insulators might be the basis of future high-speed electronic devices or other, as yet unknown, applications.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Jessica Thomas