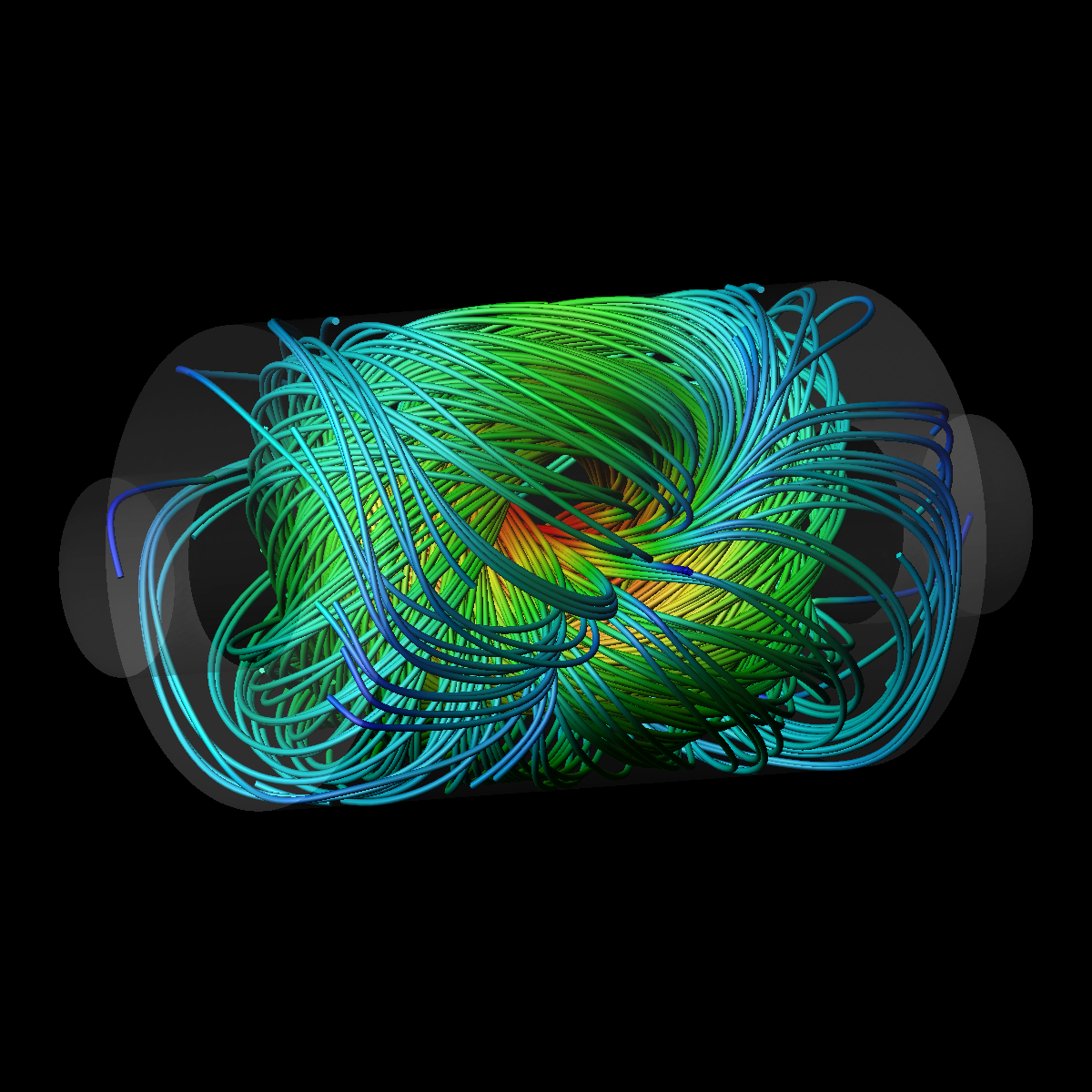
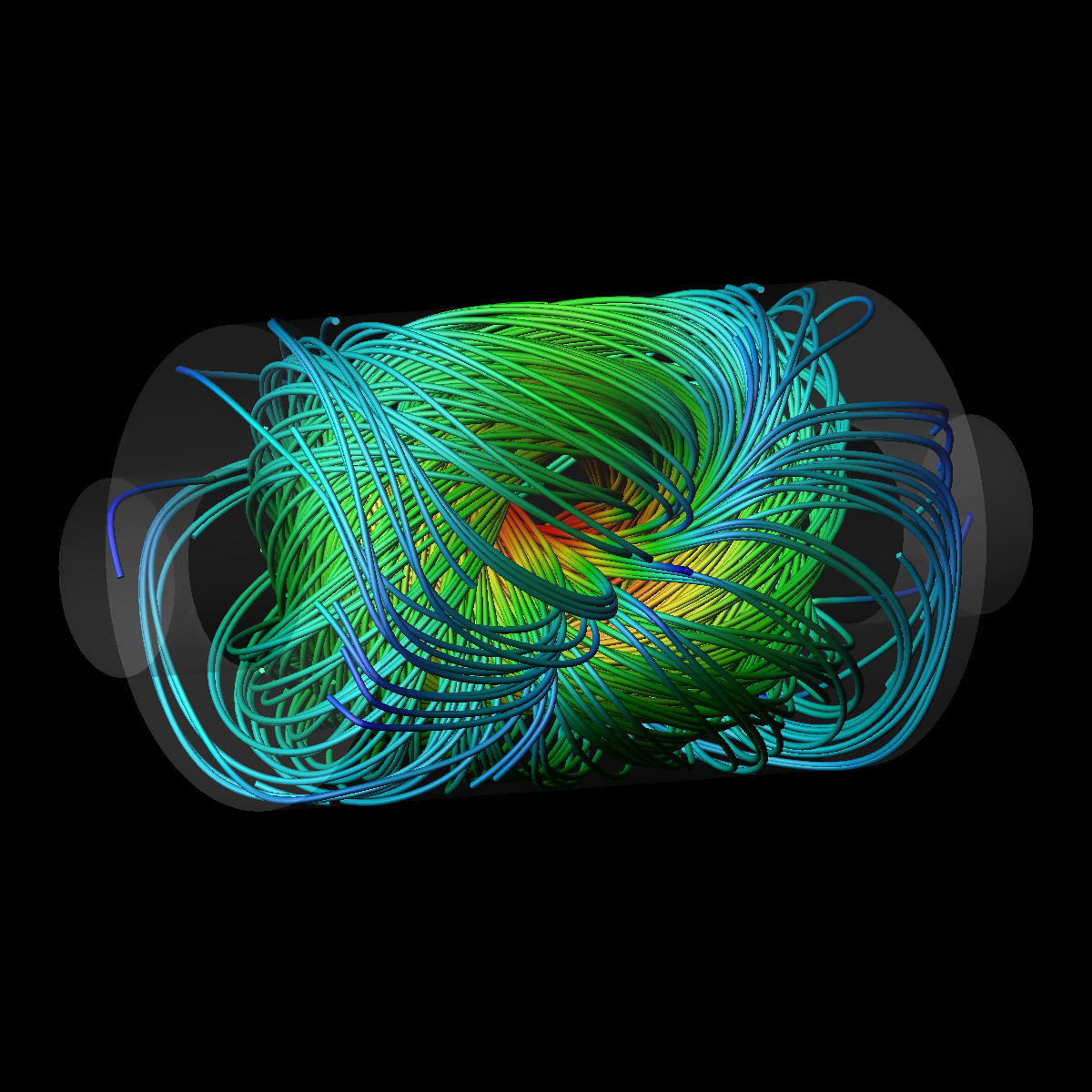
A skein of plasma
Most plasma experiments have cylindrical or toroidal symmetry, but real plasmas in the sun or the earth’s magnetosphere aren’t always so orderly. Now Chris Cothran and colleagues at Swarthmore College and collaborators at General Atomics and the University of Washington, all in the US, have shown that the charges whizzing around in a plasma sometimes prefer to generate a less symmetrical magnetic field, even when they start out in a cylindrically symmetric state. This state was predicted over years ago but was mostly ignored.
Cothran et al. sent one or two doughnut-shaped plasmas (spheromaks) into a copper cylinder, each generating its own magnetic field with axial symmetry. In both cases, the fields quickly reconfigured themselves to the same lowest-energy state: a twisted, “skein-of-yarn” structure that lacked axial symmetry but matched the team’s quantitative predictions.
This magnetic structure was determined only by a constant of the motion called helicity (the “twistiness” of the field lines remains fixed) and the dimensions of the cylinder containing the plasma. The cylinder’s length-to-radius ratio was ; similar experiments in the past have used cylinders with smaller ratios, which led to axisymmetric final states—the ones currently of interest to most researchers. The results suggest that there may be other simple and accessible plasma states that are not axisymmetric but are highly stable and possibly relevant for plasmas in space or in fusion reactors. – David Ehrenstein