The nuclear option
Atomic clock makers look for two important characteristics when they choose atoms to build their time pieces. First, the energy levels that generate the clock signal must be narrow and well defined. And second, the energy levels should be immune from external electromagnetic fields so that the clock rate doesn’t vary with, for example, position near Earth.
Several atomic species with these qualities exist, but researchers would like to take optical clocks to an even higher level of precision and stability. One approach would be to find nuclear energy levels with the right features for clocks. Nuclei have extremely sharp energy levels, but typically the excitation energies range from kilo-electron-volts to mega-electron-volts—far above the several- photon energies that are available to make optical clocks. Now, Corey Campbell, Alexander Radnaev, and Alexander Kuzmich of the Georgia Institute of Technology report in Physical Review Letters their studies of thorium nuclei that may be just right for clock building.
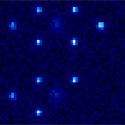
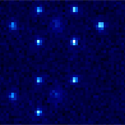
One likely candidate, thorium- , has a pair of low-lying nuclear states separated only by . As a first step in harnessing these levels, the authors trap and cool the triply charged form of - into a regular array called a Wigner crystal, which allows spatial localization of each nucleus. Future work will include addressing single ions in the crystal and spectroscopic studies of the nuclear clock transition. This could not only lead to clocks of unusual precision, but it might also help answer questions about whether fundamental physical constants are changing over time. – David Voss