Polarized Light in Safe Storage
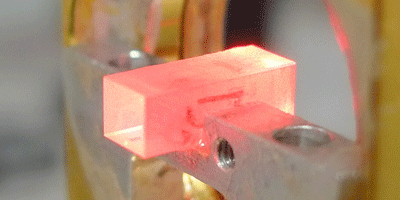
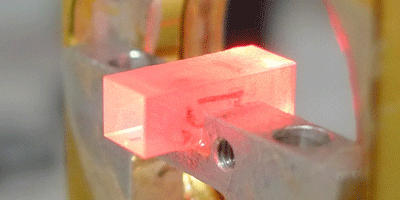
Quantum memory, which creates a place for storing quantum information until it is needed later, is an essential component in quantum computing and long-distance quantum communication. Some solid-state materials can hold quantum states of light for long times, but many materials only optimally absorb light with a certain polarization. Quantum memories that could store any polarization of light would therefore offer much more flexibility.
In a step toward this goal, three independent research groups, from China, Spain, and Switzerland, are now reporting in Physical Review Letters that they are able to store and retrieve arbitrary polarization states of light from a solid-state quantum memory. In their experiments, the teams utilized a light source limited to emit single photons, which were absorbed by rare-earth ions rigidly confined in a crystal. Each group devised a compensation technique allowing the efficient storage, for several tens to hundreds of nanoseconds, of both components of a photon’s polarization. They were able to effectively reverse the procedure to retrieve the original state.
While the groups’ compensation methods differ, they all achieve fidelities (a measure of how faithfully a state can be recovered) greater than , exceeding the maximum value achievable by a classical memory. This demonstrates that such solid-state devices could operate as quantum memories for polarization qubits. – Sonja Grondalski