Drumming to the Beat of the Vacuum
The Casimir force arises because of quantum fluctuations of the electromagnetic field in the space between two conducting plates. This leads to a radiation pressure pushing inward on the plates. The Casimir force is well studied, but a debate remains over the contributions from low-frequency fluctuations. A new experimental technique reported in Physical Review Letters reduces uncertainties about the contributions to fluctuations from surface effects by replacing one of the solid plates with a thin conducting membrane.
The calculation of the Casimir force depends on the permittivity (i.e., the electric field response) of the conductors, of which there are two competing models. The Drude model predicts that low-frequency fluctuations play no role in the Casimir force, whereas the plasma model assumes they do. Experiments with small plate separations seem to agree with the plasma model, whereas larger separations suggest the Drude model is correct.
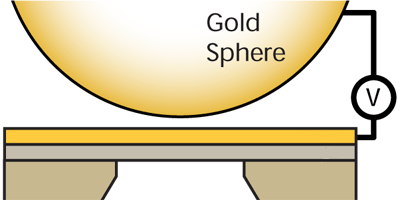
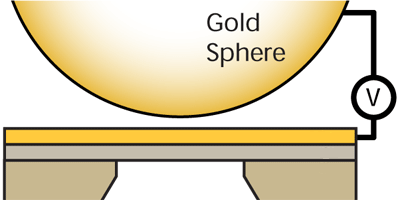
Daniel Garcia-Sanchez and his colleagues at Yale University devised a new experiment that bridges both small and large separations ( nm to microns). Their innovation is a gold-covered membrane of silicon nitride that substitutes for one conductor. The team vibrated this membrane while bringing a second conductor (a gold-covered sphere) closer to it. Observed shifts in the vibrational frequency of the membrane were due to the Casimir force, but also due to an electrostatic force coming from electrical potential differences on the membrane surface. The team corrected for this background by mapping the surface potential and thus arrived at a clean Casimir force measurement consistent with the Drude model. – Michael Schirber
Note added (11 December 2012): An Erratum and a Comment about this paper were published in Physical Review Letters.