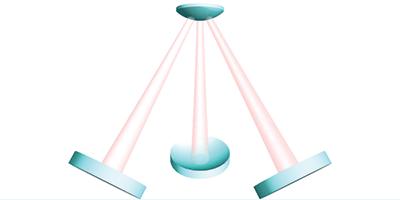
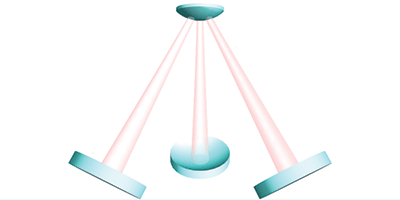
A Tripod of Light
High-precision measurements require optical elements that are extremely stable, but usually these elements are continuously jostled by mechanical vibrations from the apparatus that holds them. One way to isolate optical components would be to suspend them with light beams in souped-up versions of the optical traps used to immobilize small beads, which would also make it easier to study the components’ quantum-mechanical motion in isolation. In a typical trap, however, the levitating force arises when light scatters in a new direction. In Physical Review Letters, Giovanni Guccione and his colleagues at the Australian National University in Canberra propose suspending a mirror using light’s radiation pressure alone, without the randomness of scattering.
The researchers imagine a highly reflective convex disk that acts as the mirror at the top end of three separate optical cavities, which together form a tripod of light to levitate the disk. The amount of energy stored in light bouncing between the end mirrors of each cavity is exquisitely sensitive to the length of the cavity in comparison to the light’s wavelength. For some lengths, it turns out that any displacement of the mirror up or down generates a restoring force. The team calculates that, with just a few watts of laser power, this force is big enough to stably suspend a disk two millimeters in diameter, and that laser cooling can suppress the mechanical motions of the disk enough to reveal their quantum nature. In comparison to scattering-based levitation, the tight coupling of the motions with the light should allow more precise measurements of, for example, the strength of gravity. – Don Monroe