Neutron-Star Implosions as Heavy-Element Sources
The lightest of the chemical elements—hydrogen, helium, and lithium—were created in the hot, early phase of the Universe, about a minute after the big bang. Heavier elements were forged later—in the nuclear fires of many generations of stars and during supernova explosions [1]. But the origin of many rare chemical species, particularly the heaviest elements, remains uncertain. In particular, recent observations [2] of a nearby galaxy enriched with heavy elements challenge traditional nucleosynthesis models. George Fuller of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues [3] now propose a novel scenario for the origin of the heaviest elements, including gold, platinum, and uranium. Their hypothesis involves tiny black holes inducing neutron-star implosions and, if viable, would in one fell swoop offer solutions to other astrophysical riddles beyond heavy element synthesis.
Elements heavier than iron can be assembled only from lighter “seed” nuclei that capture free neutrons or protons [1]. Neutron capture occurs through either a “slow” s process or a “rapid” r process. In both cases, the neutron-rich nucleus undergoes beta decay, converting neutrons to protons and advancing to higher atomic numbers. The s process can proceed at the modest neutron densities available in the outer shells of evolving stars. By contrast, the r process requires 10 billion times greater neutron densities (above 1018cm−3) in order that neutron captures occur much faster than beta decay. The r process is responsible for gold, platinum, most of the lanthanides, and all of the natural actinides. The heaviest r-process nuclei—up to and beyond an atomic mass number of 240—occur through the “strong” r process, in which an iron seed captures 100 or more neutrons.
The strong r process requires a high neutron density and some combination of a large excess of neutrons over protons, very high temperatures, and rapid expansion. Such extremes are expected in supernovae—but only in rare cases [4, 5]—and in mergers between two neutron stars or between a neutron star and a black hole [6]. These compact binary mergers are estimated to be 1000 times less frequent than supernovae, but they can expel considerably larger amounts of neutron-rich matter [7, 8]—a low-rate/high-yield scenario that’s consistent with the rarity of plutonium-244 in the early Solar System and in deep-sea reservoirs on Earth [9, 10].
A wrinkle in this picture is a nearby low-luminosity dwarf galaxy known as Reticulum II, whose stars are highly enriched with strong-r-process nuclei [2]. Reticulum II is the only dwarf galaxy (out of ten) with a significant “excess” of heavy nuclei, which suggests the nuclei were produced by an infrequent event, but perhaps one not so rare as a compact-object merger [11]. Fuller and co-workers [3] therefore envision an alternative scenario in which r-process nuclei are generated in the ejected matter of a very rapidly spinning neutron star, or “millisecond pulsar,” as it implodes to form a black hole.
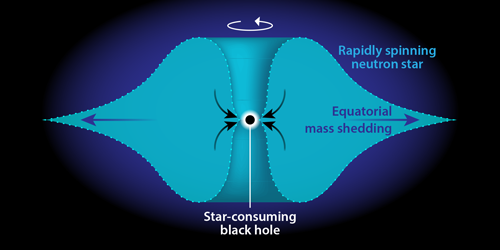
The researchers imagine that the trigger for this catastrophic collapse is a primordial black hole (PBH). Hypothetical relics from the early Universe, PBHs can have the mass of an asteroid packed into an atom-sized space and collectively they are one of several candidates for dark matter. PBHs would roam dwarf galaxies and the center of our Milky Way with a relatively high abundance, so they would collide with neutron stars at a higher rate than that of compact-object mergers. When a PBH is captured by a neutron star, it sinks towards the center and swallows the star from the inside. Then, as the growing black hole sucks in neutron-star matter, viscous shearing and magnetic fields carry angular momentum to the star’s outer layers along its equator. Fuller et al. argue that these mechanisms rip off dense nuclear matter in which the strong r process can develop (Fig. 1).
This scenario is similar to one proposed by Joseph Bramante and Tim Linden in 2016 [11]. Instead of PBHs, they proposed that dark matter particles could accumulate inside an aging neutron star to form a star-consuming black hole. As the black hole accreted mass, it would release enough gravitational binding energy to power the ejection of dense neutron matter for strong-r-process synthesis. Both teams estimated the parameters required by their models to predict implosion rates that are compatible with the r-process-enhancement of Reticulum II and the distribution of r-process elements in the Milky Way. These calculated parameters, which include, for example, dark matter density, appear to be realistic.
What’s attractive about the models presented by Fuller et al. and by Bramante and Linden is that they might simultaneously resolve a number of astrophysical conundrums. For example, the possibility that neutron stars are being routinely eaten by black holes could explain why there are far fewer pulsars at the center of our Galaxy than astrophysicists expect—though the average collapse time of a star is sufficiently long that a large population of old pulsars should still exist. In addition, both teams refer to a possibility suggested by another group [12]: The final stages of a neutron star’s demise, as well as its release of energy via the “reconnection” of its magnetic field, might be connected to recently discovered extragalactic fast radio bursts. Fuller et al. also explain the mysterious 511-keV line in the gamma-ray emission from our Galaxy’s center, linking it to positron production in the radioactively heated ejecta from a neutron-star implosion.
But while these phenomena are all consistent with the r-process scenario proposed by Fuller et al., each could be explained with less speculative (and not necessarily related) ideas. Moreover, the viability of their proposal, and that by Bramante and Linden, depends on whether the neutron stars eject sufficient mass as they collapse. Assessing this fact will require detailed relativistic hydrodynamical calculations that go beyond the coarse analytical estimates in both papers. Researchers might distinguish various scenarios by looking for a transient electromagnetic signal associated with a source that produces r-process nuclei; they would then need to use other observations to identify the source. For example, did the signal come from a region of copious dark matter, as Fuller et al. and Bramante and Linden propose, or was it accompanied by gravitational waves, as expected for inspiralling and merging compact binary stars? Such gravitational waves should be detectable by Advanced LIGO, VIRGO, and KAGRA, and they may ultimately be the smoking gun that allows physicists to solve the mysterious origin of gold.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
References
- E. M. Burbidge, G. R. Burbidge, W. A. Fowler, and F. Hoyle, “Synthesis of the Elements in Stars,” Rev. Mod. Phys. 29, 547 (1957).
- A. P. Ji, A. Frebel, A. Chiti, and J. D. Simon, “R-process Enrichment from a Single Event in an Ancient Dwarf Galaxy,” Nature 531, 610 (2016).
- G. M. Fuller, A. Kusenko, and V. Takhistov, “Primordial Black Holes and r-Process Nucleosynthesis,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 061101 (2017).
- C. Winteler, R. Käppeli, A. Perego, A. Arcones, N. Vasset, N. Nishimura, M. Liebendörfer, and F.-K. Thielemann, “Magnetorotationally Driven Supernovae as the Origin of Early Galaxy r-Process Elements?,” Astrophys. J. Lett. 750, L22 (2012).
- P. Banerjee, W. C. Haxton, and Y.-Z. Qian, “Long, Cold, Early r Process? Neutrino-Induced Nucleosynthesis in He Shells Revisited,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 201104 (2011).
- J. M. Lattimer, F. Mackie, D. G. Ravenhall, and D. N. Schramm, “The Decompression of Cold Neutron Star Matter,” Astrophys. J. 213, 225 (1977).
- C. Freiburghaus, S. Rosswog, and F.-K. Thielemann, “r-Process in Neutron Star Mergers,” Astrophys. J. Lett. 525, L121 (1999).
- A. Bauswein, R. Ardevol Pulpillo, H.-T. Janka, and S. Goriely, “Nucleosynthesis Constraints on the Neutron Star-Black Hole Merger Rate,” Astrophys. J. Lett. 795, L9 (2014).
- A. Wallner et al., “Abundance of Live 244Pu in Deep-Sea Reservoirs on Earth Points to Rarity of Actinide Nucleosynthesis,” Nat. Commun. 6, 5956 (2015).
- K. Hotokezaka, T. Piran, and M. Paul, “Short-Lived 244Pu Points to Compact Binary Mergers as Sites for Heavy r-Process Nucleosynthesis,” Nat. Phys. 11, 1042 (2015).
- J. Bramante and T. Linden, “On the r-Process Enrichment of Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies,” Astrophys. J. 826, 57 (2016).
- J. Fuller and C. D. Ott, “Dark Matter-Induced Collapse of Neutron Stars: A Possible Link Between Fast Radio Bursts and the Missing Pulsar Problem,” Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 450, L71 (2015).