A Laser-Free Method for Cooling Heavy Molecules
While smashing together charged particles at high speeds might be the tried-and-true method for discovering new physics, an alternative approach based on precise measurements of very-low-energy molecules—particularly those containing a heavy atom—is gaining ground. However, most methods of decelerating and trapping those molecules rely on laser cooling and only work for molecules with specific energy structures. Steven Hoekstra of the University of Groningen, Netherlands, and his colleagues have now decelerated a beam of neutral diatomic molecules to a standstill using only electric fields [1]. The molecules, strontium monofluoride (SrF), are the heaviest by a factor of 3 to be stopped using this technique.
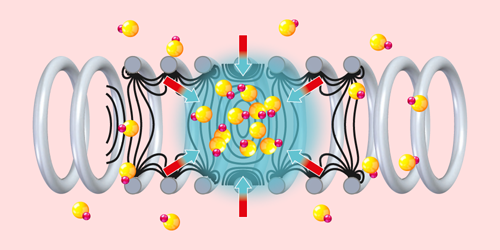
The researchers generate a cloud of SrF molecules using a cryogenic buffer gas beam source, yielding a beam moving at the relatively slow speed of 190 m/s. The molecules then enter a device called a traveling-wave Stark decelerator, where thousands of high-voltage, ring-shaped electrodes create a moving electric-field pattern that travels along a 4.5-m-long chamber. As the molecules are captured by local minima in the moving field, they lose kinetic energy, but only by combining a record-length Stark decelerator with a beam that was already slow to begin with could the team bring the molecules to a standstill.
By holding the SrF molecules stationary for 50 ms, Hoekstra and colleagues have shown how to expand the range of species that can be used for collision studies, precision measurements, and trapping experiments. Next, they hope to use this technique to look for slight asymmetries in interactions involving the electrons of barium monofluoride—a molecule even heavier than SrF. Such effects could indicate an electric dipole moment greater than that predicted by the standard model, suggesting new physics.
–Rachel Berkowitz
Rachel Berkowitz is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Vancouver, Canada.
References
- P. Aggarwal et al., “Deceleration and trapping of SrF molecules,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 173201 (2021).