Using Fluctuations to Measure Beam Properties
Scientists planning future particle accelerators and synchrotron light sources strive for tighter, more powerful electron beams. But as beams get narrower, it becomes harder to measure properties such as their size and angular divergence—vital information for predicting their performance and for accurately interpreting experimental results. Now, Ihar Lobach of the University of Chicago and colleagues have demonstrated a new way to measure a beam’s vertical emittance—an important parameter that represents the beam’s size and spread—more precisely than existing methods [1, 2].
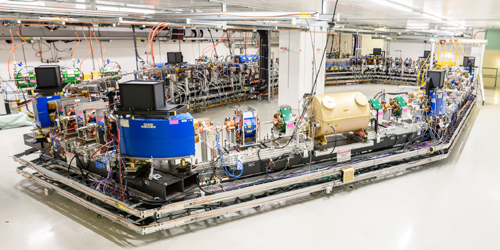
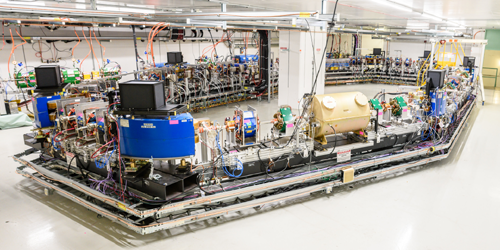
The team tested their method at the Integrable Optics Test Accelerator (IOTA) at Fermilab. At this facility, an electron bunch circulating around a particle storage ring passes through an undulator—a sequence of alternating magnetic fields that “wiggles” the electrons from side to side, making them emit a radiation pulse. Although the number of electrons circulating in the ring remains constant, variations in the electrons’ positions and directions of motion produce tiny fluctuations in the radiation intensity from one lap of the ring to another.
Lobach and colleagues measured these intensity fluctuations using a circuit that splits the radiation pulses and delays one branch by exactly the period of one lap. This delay allowed them to subtract one intensity measurement from another one made during the consecutive lap. They fed the resulting fluctuation values into a theoretical model that relates the radiation intensity fluctuations to the electron beam’s vertical emittance (and several other parameters) to determine the vertical emittance of the electron beam.
While the IOTA undulator produces infrared radiation, the researchers say that a key feature of their technique is that it can be used for synchrotron light sources of any wavelength. This feature is important, because synchrotrons are often used as x-ray sources for research in a range of fields, from biology to materials science.
–Erika K. Carlson
Erika K. Carlson is a Corresponding Editor for Physics based in New York City.
References
- I. Lobach et al., “Transverse beam emittance measurement by undulator radiation power noise,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 134802 (2021).
- I. Lobach et al., “Measurements of undulator radiation power noise and comparison with ab initio calculations,” Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams 24, 040701 (2021).