Spin Control Without Magnetic Fields
In graphene, spin currents can live much longer than they can in other materials, making the material an ideal platform for future spintronic devices. But there is a problem: To manipulate graphene’s spin currents, researchers need to apply a magnetic field to the material. The necessary hardware is difficult to integrate into circuits, limiting how small graphene-based spin devices could be shrunk. Now Josep Ingla-Aynés of the Nanoscience Cooperative Research Center (CIC NanoGUNE), Spain, and colleagues have demonstrated a method to manipulate—at room temperature—graphene spin currents using only electric fields [1].
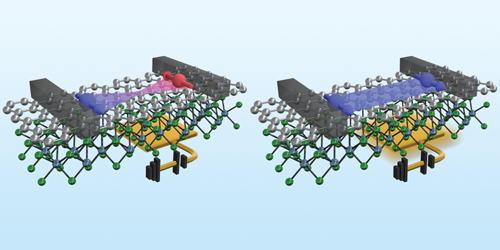
The team stamped a sheet of tungsten diselenide on a sheet of bilayer graphene and heated the two materials to bond them together. Then they patterned the structure with a series of electrodes, which they used to apply an in-plane electric field and a gate voltage and to inject a spin current into the graphene. Experiments were performed at 50 K and at room temperature.
At both temperatures, the team observed that they could switch the polarization direction of the spin current by changing the magnitude of both the in-plane electric field and the gate voltage. They say that the control comes from the presence of spin-orbit coupling in the tungsten diselenide layer. This effect produces an effective magnetic field in the graphene that is sufficient to change the spin angle.
Ingla-Aynés says that the demonstration represents a room-temperature version of the long-sought-after “Datta Das” spin transistor. The Datta Das spin transistor is a device whose electrical resistance can be switched from high to low by changing the polarization direction of the spin current. Such devices have been realized at low temperatures using two-dimensional electron gases but not at higher temperatures.
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is the Deputy Editor of Physics Magazine.
References
- J. Ingla-Aynés et al., “Electrical control of valley-Zeeman spin-orbit-coupling-induced spin precession at room temperature,” Physical Review Letters 127, 047202 (2021).