Colloids Reproduce Interatom Interactions on Surfaces
Many components in today’s technologies are built by controlling the assembly of elementary building blocks. For example, in “epitaxy,” components are usually made by depositing atoms layer-by-layer onto a substrate. Epitaxy methods also exist for larger systems, such as micrometer-diameter colloids. Now Manodeep Mondal and Rajesh Ganapathy of Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, India, show that interactions among epitaxially deposited colloids follow predictions made for atomic systems [1]. They say that the finding could help to improve nanofabrication methods.
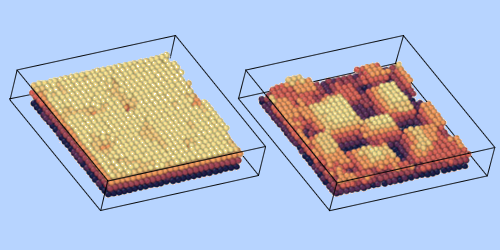
In their experiments, Mondal and Ganapathy deposited colloids onto substrates patterned with square arrays of holes. The hole spacing varied between substrates and differed slightly from the preferred colloid spacing. The duo mapped the effect of the resulting “misfit” strain on the growth of the colloidal structures using microscopy measurements.
For low misfit strains, they found that the rate of colloid diffusion across the substrate remained constant with increasing structure height. They also found little distortion of underlying layers as new ones formed on top. For high misfit strains, they found that the diffusion rate varied significantly with structure height and that distortion effects influenced how the structures developed. For example, for misfit strains of 4.5%, they found that interactions among colloids warped the underlying substrate, leading to more patchy structures. The results match predictions for atomic systems, which, being 10,000 times smaller than the colloids used in these experiments, are nearly impossible to track in this way.
“It is always a delight to directly observe and quantify an effect anticipated by theory and simulations,” Ganapathy says. “We are particularly excited about the wide range of length scales over which similar physics seems to work.”
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is the Deputy Editor of Physics Magazine.
References
- M. Mondal and R. Ganapathy, “Direct measurements of surface strain-mediated lateral interactions between adsorbates in colloidal heteroepitaxy,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 088003 (2022).