The Aerodynamics of Perching Birds
The claim that physicists are stumped by the aerodynamic impossibility of bumblebee flight is, of course, just a myth (see Focus: Bumblebees In Turbulence). But there are still mysteries about the flight of other animals. Now, Dibya Raj Adhikari and colleagues at the University of Central Florida consider one such mystery—why some birds angle their wingtips backwards when they execute a “perching” maneuver just before landing [1]. The team finds that this “swept-wing” posture increases the lift generated by the wings, a result that could help engineers design safer aircraft.
Typically, as a bird prepares to land, it decelerates while heaving its wings downwards and pitching the front edges upwards. Physicists have investigated various aspects of this maneuver, but they don’t fully understand what happens when it is combined with a swept-wing posture.
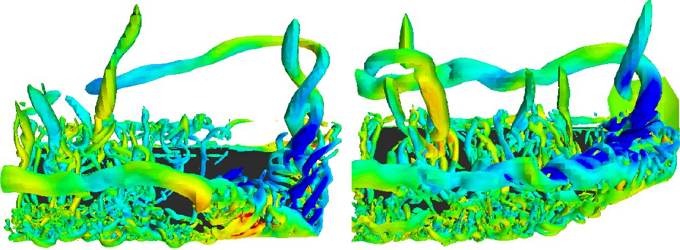
To address this problem, Adhikari and his colleagues conducted experiments that involved pushing aluminum plates through a tank of water containing 10- 𝜇m-wide, 10- 𝜇m-wide, silver-coated glass spheres. In one experiment, they used a rectangular plate (straight wing); in the other they used a tapered plate (swept wing). They moved the plates at a constant speed for a few seconds, then decelerated them while tilting them and shifting them towards the tank wall, a sequence meant to simulate a bird slowing while pitching and heaving its wings as it approaches the ground.
Force measurements show that the tapered plate produced more lift than the rectangular plate. Simulations and observations of the glass spheres reveal that this increase came from a lift-enhancing “leading-edge” vortex. This vortex formed on both plates, but for the tapered (swept-wing) plate, a lateral flow towards its tip stabilized the vortex, preventing its decay.
–Marric Stephens
Marric Stephens is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Bristol, UK.
References
- D. R. Adhikari et al., “Effect of wing sweep on a perching maneuver,” Phys. Rev. Fluids 7, 044702 (2022).