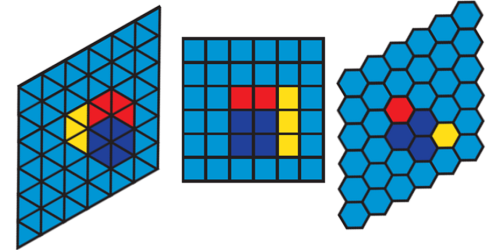
Shape Matters in Self-Assembly
Many biological structures form through the self-assembly of molecular building blocks. A new theoretical study explores how the shape of these building blocks can affect the formation rate [1]. The simplified model shows that hexagonal blocks can form large structures much faster than triangular or square blocks. The results could help biologists explain cellular behavior, while also giving engineers inspiration for more efficient self-assembly designs.
Certain viruses and cellular structures are made from self-assembling pieces that can be characterized by geometrical shapes. For example, some types of bacteria host carboxysomes, which are icosahedral (20-face) compartments built up from self-assembling hexagonal and pentagonal subunits.
To investigate the role of shape, Florian Gartner and Erwin Frey from Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich simulated self-assembly of two-dimensional structures with three types of building blocks: triangles, squares, and hexagons. The model assumed that the blocks bind along their edges, but these interactions are reversible, meaning that the resulting structures can fall apart before growing very large. Gartner and Frey found that certain shapes were better than others at assembling into larger structures, as they tended to form intermediate structures with more bonds around each block. In particular, hexagonal blocks were the most efficient building material, forming 1000-piece structures at a rate that was 10,000 times faster than triangular blocks.
The results are not limited to geometrically simple shapes. “Our insights hold relevance beyond these simplified models, extending to a wide range of biological and nanotechnological self-assembly processes,” Frey says. He and Gartner think that engineers could improve the efficiency of nanofabrication by choosing building blocks with optimized shapes and binding-site locations.
–Michael Schirber
Michael Schirber is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Lyon, France.
References
- F. M. Gartner and E. Frey, “Design principles for fast and efficient self-assembly processes,” Phys. Rev. X 14, 021004 (2024).