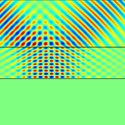
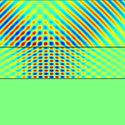
Isotropy can’t be swept under a carpet cloak
Invisibility cloaks—optical materials that hide objects by distorting the path of light or altering its scattering pattern—have captured the imagination of scientists and the public alike. Unfortunately, an obstacle to manufacturing cloaks is the need to make them from anisotropic materials, which are difficult to engineer at optical frequencies.
In 2008, Li and Pendry [1] proposed the idea of a “carpet cloak,” whereby the hidden object lies under a smooth bump that appears flat to the observer. In principle, the carpet cloak must also be made of an anisotropic material, but Li and Pendry showed that even side-stepping this requirement, one can obtain cloaking, albeit as an approximation to the exact problem.
But could the isotropic approximation introduce image distortions large enough to give away the cloaking effect? Writing in Physical Review Letters, Baile Zhang, Tucker Chan, and Bae-Ian Wu at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in the US trace a light ray reflected from an isotropic carpet cloak. They find an isotropic cloak preserves the phase but not the direction of the scattered light. Instead, the ray is shifted laterally—in some cases by an amount comparable to the object itself—leaving a telltale signal that what appears as empty space may be the presence of an object.
Zhang et al.’s efforts to outline the fundamental and practical limitations of using isotropic media instead of anisotropic ones should inform the search for broadband, optical cloaks, as well as a wide range of devices and applications in transformation optics. – Manolis Antonoyiannakis
[1] J. Li and J. B. Pendry, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 203901 (2008).