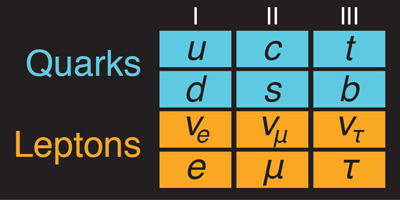Particle Families Come in Three
The fundamental fermions belong to three families, but physicists don’t know why there aren’t more. A new theory presented in Physical Review Letters imagines that our universe has an extra spatial dimension that is “off-limits” to particles in a similar way that the interior of materials called topological insulators is off-limits to conducting fermions. This geometrically based formulation could naturally produce three families, and may make testable predictions about neutrinos and the Higgs boson.
Each family in the standard model of particle physics includes four members. The lightest family, for example, consists of the electron, the electron neutrino, the up quark, and the down quark. The other two families are progressively more massive. Nothing in the standard model rules out more families at higher and higher mass, but experimental evidence suggests that three is all there is.
As a way to explain this family tree, David Kaplan and Sichun Sun at the Institute for Nuclear Theory in Seattle, Washington, borrow an idea from condensed-matter physics and assume that spacetime resembles a topological insulator. These unique materials are insulators on the inside, but with free fermions conducting along the outer surface. By assuming a certain topology within an analogous, higher dimensional “insulator,” the authors can produce exactly three families of particles confined to the four-dimensional surface. Specific particle properties in the standard model, such as masses and couplings, could be the result of how these wave functions extend a small distance into the hidden extra dimension. – Michael Schirber