Giving Graphene a Rest
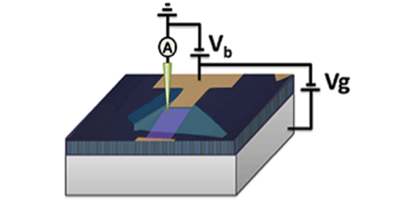
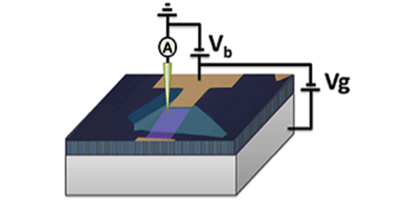
A pristine sheet of graphene has many interesting electronic properties, but they can be lost when the material is supported on a substrate, as it has to be in most experiments and practical devices. The best substrates so far—graphite and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN)—both have limitations; in particular, hBN is known to cause a spatial modulation in graphene’s electronic structure. Now, researchers in Eva Andrei’s group at Rutgers University, New Jersey, have identified molybdenum disulfide ( MoS2), a semiconductor that cleaves easily into atomically smooth sheets, as a promising substrate. The material could be particularly well suited as a substrate in spintronics devices, which require a perfect landscape for graphene’s electrons.
Andrei and her colleagues rested a strip of graphene on a MoS2 flake that was deposited on a thick insulator. (In this geometry, a voltage applied to the insulator can be used to control the density of graphene’s charge carriers.) Graphene, either as a standalone sheet or on another surface, would normally tend to buckle, reducing the mobility of its electrons. But the team showed with scanning probe microscopy that when graphene is supported on MoS2 these warps are as small as in the case of hBN, yet without the undesired effects on graphene’s electronic properties. The authors also placed the structures in a magnetic field to show that they could obtain clean, quantized circular orbits—a sign that electrons can travel a long length (approximately 30 nanometers) before scattering.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Jessica Thomas