Superconducting Antennas Tune In
Metamaterials have been used to build more efficient and directional radio-frequency (rf) antennas for wireless communications. Most schemes, however, work at one fixed frequency and require impractically large components for operation at a few megahertz (MHz)—a frequency range that can be reflected by the Earth’s ionosphere and is thus suitable for long-range communications. Now, a team led by Steven Anlage at the University of Maryland, College Park, has demonstrated a new metamaterial, made with superconducting elements, that could be used to build tunable and efficient rf antennas.
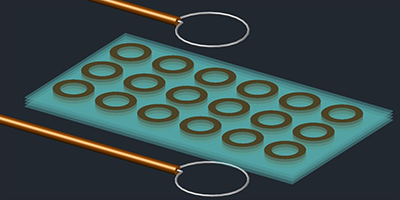
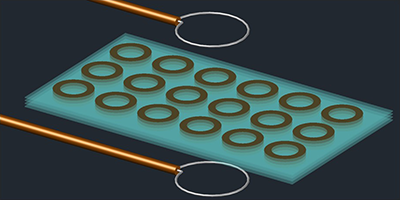
The device consists of two-dimensional arrays of spirals made of niobium, a superconductor with a critical temperature ( Tc) of 9.2K. Several arrays are stacked on top of each other to form a three-dimensional structure, which was placed between transmitting and receiving antennas to study its electromagnetic response. Below Tc, each spiral acts like an inductor-capacitor circuit with a sharp resonance. In isolation, each spiral resonates at 25MHz, but the coupling between multiple spirals shifts the resonance of the entire structure to lower frequencies. The authors demonstrated that this resonance can be tuned over a ∼0.25-MHz range by varying the temperature by a few degrees. The effect occurs because temperature controls the density of superconducting electrons and thus the effective inductance of each resonator. The metamaterial structure could be placed near a radio-frequency source to improve the source’s coupling to free space and boost its efficiency.
This research is published in Physical Review Applied.
–Matteo Rini