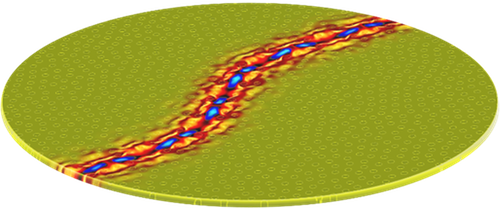
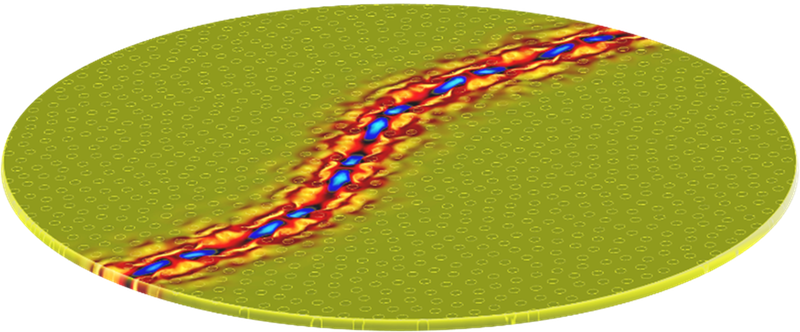
Image—Sound Waves Guided Along Curvy Path
Phononic crystals are arrays of rods or spheres that use interference effects to manipulate vibrational waves for purposes such as audio filters, ultrasound imaging, or sound proofing. Now researchers provide a visualization of a computer simulation showing that a bit of randomness in the placement of these elements allows sound waves to be guided along curvy paths. The team says that such arbitrary paths could be useful for routing acoustic signals in future phononic integrated circuits.
A wave traveling through a perfectly repeating set of scattering sites can interfere with itself and become blocked from propagation over a range of frequencies called the band gap. A photonic crystal exploits this effect to corral light waves. For example, if you remove a line of scatterers in a photonic crystal, you create a wave channel (waveguide), but it’s usually restricted to straight lines and right angles.
Recently, researchers have studied “hyperuniform” photonic structures, from which arbitrarily shaped waveguides can be made. The scattering elements in these structures don’t form a perfectly repeating pattern, but the spacing between them doesn’t vary very much. Hyperuniform structures maintain the large band gap found in periodic photonic crystals, but also have other benefits.
Marian Florescu and his colleagues at the University of Surrey, UK, have now shown with computer simulations that a hyperuniform structure for vibrational waves—a phononic structure—can also have a large band gap. But the team was surprised to find additional properties beyond those of photonic structures. For example, one can create resonant cavities within the phononic structure that have “quality” or “Q” factors as high as 1015, meaning that a wave with frequency 10 GHz could remain trapped for roughly 8 hours. These high Q values lead to waveguiding that is highly efficient, with nearly 100% transmission of the acoustic waves from beginning to end of a curvy waveguide.
This research is published in Physical Review B.
–David Ehrenstein
David Ehrenstein is a Senior Editor for Physics Magazine.