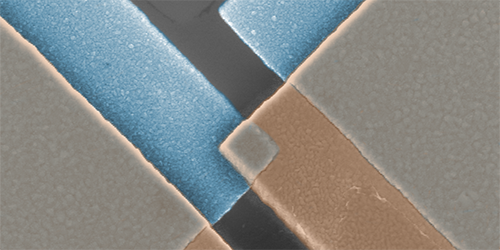
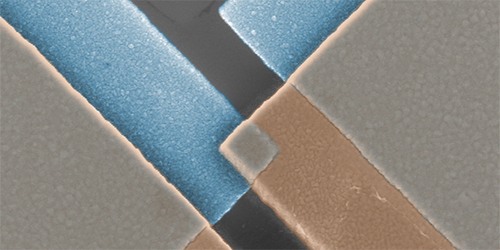
On-Chip Thermometer
A new micrometer-scale thermometer—small enough to fit on a computer chip—can measure temperatures as low as 7 millikelvin, which is a tenfold improvement over similar designs. The device works by monitoring the current that tunnels between a metal and a superconductor layer. With its ability to measure cryogenic temperatures, this chip-compatible thermometer might eventually be used to thermally monitor qubits in a solid-state quantum computer.
A tunnel junction consists of two conductors (metal or superconducting) separated by an insulating barrier. The rate by which electrons tunnel through the barrier is dependent on temperature. In recent years, scientists have created devices, such as the Coulomb blockade thermometer, which use tunnel junctions to measure temperature, but the tunnel configurations are often complicated and require sophisticated methods to extract a temperature reading.
Researchers from Aalto University in Finland and the University of Basel in Switzerland designed a new thermometer that can reach millikelvin temperatures with a compact experimental setup. For the core of their device, the team fabricated a 400-nanometer-wide normal-metal–insulator–superconductor (NIS) tunnel junction from thin layers of copper, aluminum oxide, and aluminum. The team measured the tunneling current ( ) at different voltages ( ) and then used the shape of the - curve to estimate the temperature of the copper layer (which also acts as the thermal contact to a sample). The temperature sensitivity is better than previous NIS-based systems because the new design provides shielding from radiation and electronic noise, while the chip layout allows efficient evacuation of dissipated heat.
This research is published in Physical Review Applied.
–Michael Schirber