Termite Skyscrapers
Termites are the high-rise builders of the bug world, with nests that can stretch several meters towards the sky. Thousands of the insects work together to construct an interconnected network of chambers and tunnels from excavated soil for a colony to live in. Now researchers have developed a model that shows how termites, aware only of their immediate vicinity, can build such large-scale, functional structures without a blueprint. The authors suggest the same model could be used to control and direct an army of efficient robotic builders without central supervision.
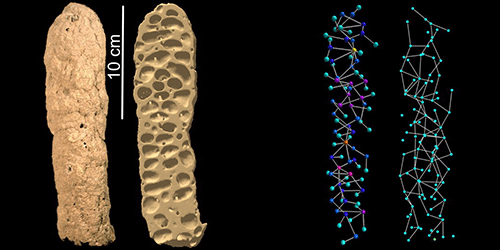
In the model used by Young-Ho Eom, from the IMT Institute for Advanced Studies in Italy, and colleagues, the growth of a nest initiates with a single tunnel that starts underground and terminates in a chamber. A series of rules then determine how the rest of the nest forms: New tunnels can emerge from any existing chamber, but they are most likely to stem from the most recently built chambers. The direction and length of each new tunnel is assigned according to distributions found in real nests. And each tunnel ends in a new chamber from which more tunnels can appear. In addition, less frequently used tunnels are chosen at random to become blocked, and neighboring chambers are merged together. The authors demonstrate that nests simulated according to these “local” rules share structural attributes—such as the shortest path connecting any two chambers—with termite nests found in Africa.
This research is published in Physical Review E.
–Katherine Wright