Like Prefers Like, Except in a Virus
Influenza and certain other viruses have a segmented genome, in which each segment is a strand of RNA that codes for a particular protein. New viruses forming from the many genome copies in an infected cell must amass one of each type of segment—and no duplicates—in order to go on to infect other cells and replicate. A better understanding of how segments recognize each other to form a complete genome could therefore lead to new antiviral drugs. In Physical Review Letters, Sergey Venev and Konstantin Zeldovich at the University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, use a simple statistical model to predict the most efficient segment-signaling mechanism for avoiding duplicated genetic material.
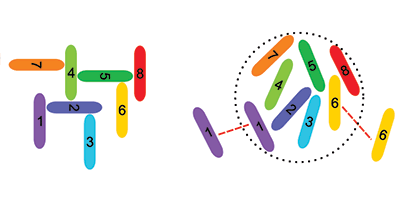
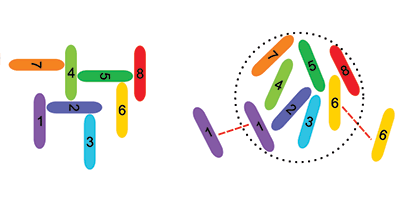
Venev and Zeldovich used a Monte Carlo algorithm to simulate the evolution of influenza A—a virus with eight segments in its genome—over generations. Their starting assumption was that each of the eight RNA segments had a random affinity for the other seven and itself. In each new generation of viruses, the segments were allowed to mutate, but only if these mutations increased the probability that a daughter virus had exactly eight unique segments.
The researchers found that identical segments evolved to repel each other—a surprise since it is generally believed that it is attractions between dissimilar segments that ensure a complete genome. Only high-resolution structural studies of viral genomes can reveal the true segment signaling mechanism, but Venev and Zeldovich’s work shows an interesting application of statistical physics to evolutionary biology. – Jessica Thomas