Computing with Entangled Ions
Quantum computing typically involves manipulating quantum bits of information without observing them—at least until the final readout. An alternative strategy is to measure qubits throughout the process, and use each observation as part of the computation. Previous experiments in measurement-based quantum computing (MBQC) have used photons, which are hard to prepare in large numbers. Now, for the first time, researchers have performed MBQC with trapped ions. As reported in Physical Review Letters, the team entangled several ionic qubits and then demonstrated a set of basic ion measurements that can be combined to produce any arbitrary computation.
Most quantum computer designs try to mimic classic computers with a sequence (or circuit) of devices called gates. These gates can change the state of a qubit or correlate one qubit with another (entanglement). However, most gates don’t measure anything because that would destroy the quantum information held by the qubits.
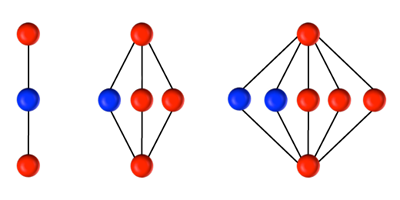
By contrast, MBQC involves a sequence of single-qubit measurements performed on a “cluster” of entangled qubits. The entanglement allows measurement of a particular qubit (or qubits) to have the effect of a gate operation on one of the not-yet-measured qubits. Moreover, the outcome of one measurement in the sequence can dictate how subsequent measurements are made.
Ben Lanyon of the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information in Innsbruck, Austria, and colleagues have built an MBQC system with trapped ions. The team placed up to seven calcium ions in a linear trap and entangled them through laser interactions. They then showed that specific measurement sequences could reproduce a basic set of gate operations, as well as correct for errors coming from qubits interacting with the environment. – Michael Schirber