Exploding Cavities
Not every planetary crater is the result of meteorite impact. They can also form, for example, when a pocket of hot steam trapped in magma is suddenly released. A new experimental study shows that craters resulting from underground air cavity explosions have much smoother outer rims than craters formed from the impact of a large object. These results could help scientists identify the origin of planetary craters and better understand planetary terrains.
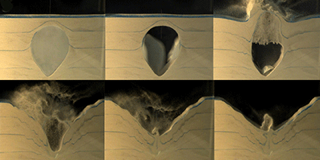
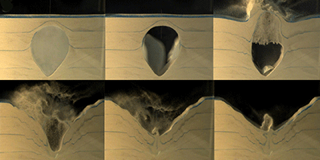
Felipe Pacheco-Vázquez and colleagues from the Meritorious Autonomous University of Puebla (BUAP) in Mexico inflated centimeter-sized balloons with air and covered them with sand. They popped the balloon and recorded the dynamics of the resulting cavity formation on video. When released from the balloon, the air from the underground cavity rose and pushed the overlying sand upwards. The pressure from this air eventually caused the resulting mound to explode, sending sand grains upwards in a corona. Grains from the corona fell back into the empty cavity as its sides collapsed inwards. Finally a jet of sand rose up from the middle of the crater and then dropped leaving a central sand pile.
The researchers experimented with different air pressures, cavity volumes and balloon depths. But they always observed that the expelled sand fell back into the cavity void, leaving a crater with a flat rim. This feature, they suggest appears to be an identifying characteristic of exploding air cavities In contrast, the impact of a meteorite causes material to splash outwards, leaving a raised ring of debris around the edge.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Katherine Wright