Seeing a Bond’s Polarity
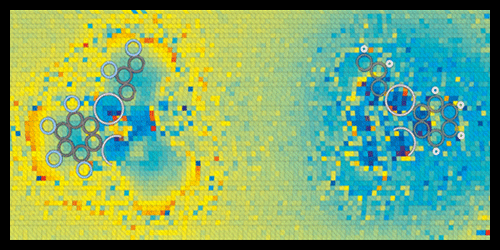
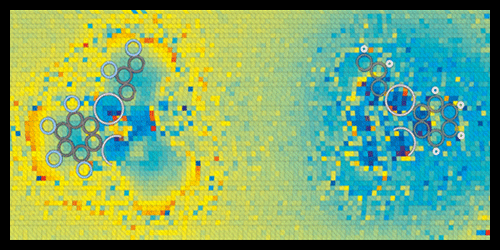
Scanning probe techniques like atomic force microscopy (AFM) provide researchers with a window into the nanoworld, allowing them to image and manipulate molecules with atomic precision. A recent offspring of AFM, called Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy (KPFM), can also probe the charge on individual atoms and distinguish different types of chemical bonds. Now, a team led by Jascha Repp at the University of Regensburg has pushed the charge-imaging capabilities of scanning microscopy even further, showing that a new variation of AFM can observe the subtle charge imbalances that determine the polarity of chemical bonds.
KPFM maps charge distributions by scanning a cantilever tip, biased at a certain voltage, over a sample surface to measure its work function—the energy needed to remove an electron. The work function yields information on dipoles and charges at the surface. However, to resolve individual bonds, the tip has to be so close to the sample that it might penetrate the electron shells of the sample molecules. In this regime, the complex set of forces acting on the tip make the measured signals hard to interpret. To address this challenge, the authors designed a microscopy scheme that disentangles the various forces through a series of measurements performed as a function of the bias voltage and distance between tip and sample.
Repp and co-workers tested the technique on two organic compounds of mercury, which should contain, according to calculations, chemical bonds of different polarities: C-F and C-H. The acquired charge-distribution images revealed molecular charge separations with unprecedented resolution. In agreement with theoretical expectations, the researchers found that F atoms pull electron charge from C electrons, giving the C-F bonds a large polarity, while C-H bonds have a smaller polarity of opposite sign.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Matteo Rini