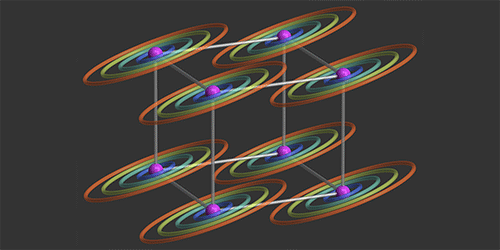
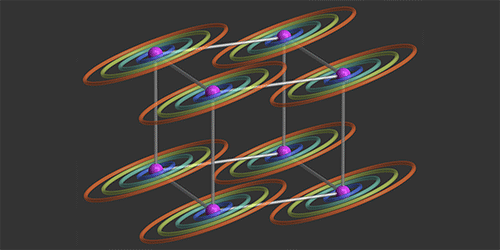
The Quantum Hall Effect Leaves Flatland
The quantum Hall effect (QHE) is now sufficiently “standard” that it’s the basis for a unit of measure (the ohm). But more exotic offshoots of this famously 2D phenomenon have yet to be explored, such as a 4D version predicted in 2001. This hyperdimensional “topological” material is predicted to host relativistic-like particles that carry electric current along its 3D surfaces, an effect that’s difficult to isolate in a regular solid. A way to observe the 4DQHE in a cold atomic system has now been proposed by a team of theorists from the Bose-Einstein Condensate Center in Trento, Italy, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) in Zurich, and the Université libre de Bruxelles, Belgium.
The 4DQHE can emerge in a 4D lattice when magnetic fields pierce two orthogonal lattice planes. To engineer an analogous situation in an atomic system, the authors imagine trapping atoms in a 3D optical lattice and then stretching it into a synthetic fourth dimension. This is possible thanks to a relatively new approach that involves using a laser to couple the internal states of an atom in such a way as to simulate the presence of an extra spatial dimension. Finally, the researchers would harness established atom-manipulation techniques based on lasers to generate “artificial” magnetic fields.
If experimentalists implement this idea, they’ll need a measurable signature of the 4DQHE in a 4D lattice. The authors suggest detecting the speed with which an atom cloud drifts through the lattice, as its value should be characteristic of the 4DQHE topology.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Jessica Thomas