Capillary Effect in Grains Explained
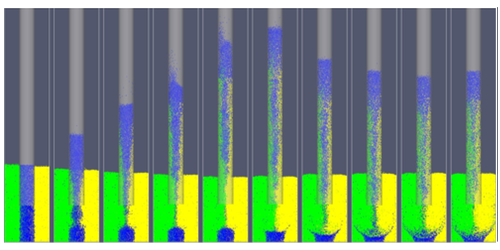
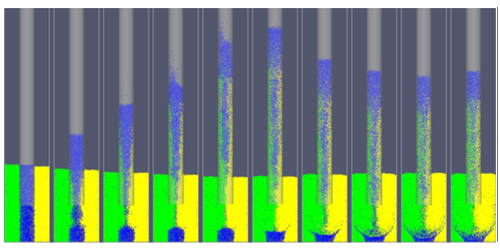
When a narrow tube is inserted into a bed of vibrating grains, the granular material rises up inside the tube, much like a liquid climbs through a thin straw. For liquids, this capillary, or wicking, action results from attractive interactions between the liquid molecules and the tube walls. But that explanation does not apply to grains—they do not stick to walls with enough force to defy gravity. New computer simulations show that the effect instead relies on friction-induced convective motion in the vibrating grains.
Fengxian Fan, from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, and colleagues simulated a rectangular container partly filled with spherical grains (0.6 mm diameter). In the center of the container, a cylindrical tube (8 mm diameter) descended into the grains. When the tube was vibrated up and down, the simulated grains rose up the tube to a height of around 50 mm. But the effect disappeared when the team made the container walls frictionless. Wall friction causes a well-known convective motion in shaken grain systems (called the Brazil nut effect) in which grains at the walls are pushed downward, while grains in the center move up. The team showed that when the inserted tube vibrates, the resulting grain convection produces a pressure in the bottom of the tube that pushes material upwards. This understanding might help in the design and development of a grain pump that could transport grains along pipes for industrial processes.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Michael Schirber
Michael Schirber is a Corresponding Editor for Physics based in Lyon, France.