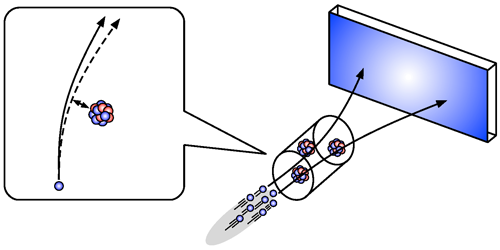
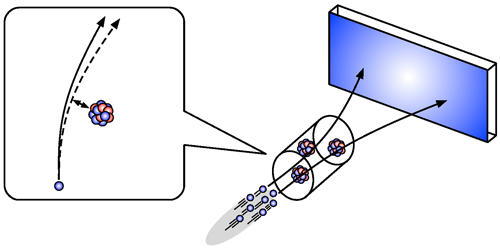
Neutron Test for Newton’s Gravity
Newton’s law of universal gravitation predicts that the gravitational force between two objects is proportional to the objects’ masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The law, which applies to weakly interacting objects traveling at speeds much slower than that of light, has survived test after test. However, some quantum gravity theories anticipate that the law might break down at small distances. Now, through experiments with a pulsed neutron beam, Christopher Haddock of Nagoya University, Japan, and colleagues have checked Newton’s law on subnanometer scales. So far, the team has found no deviations from Newtonian predictions.
The team fired pulses of neutrons at a chamber filled with either helium or xenon gas and monitored both the travel time of the neutrons through the gas and the neutrons’ scattering angles. From these measurements, they reconstructed the scattering process with the aid of simulations. They found that the scattering-angle distribution fit the predictions—based only on known laws of physics—for neutrons bouncing off gas nuclei. This result indicates that, within the sensitivity of the experiment, no unexplained force—be it modified gravity or another type of interaction—acts on length scales below 0.1 nm. However, the researchers were only able to determine an extremely large upper limit on the strength of such a force: 1024 times that of gravity. Still, this is the strictest limit set by any experiment on these spatial scales. The team is currently upgrading the setup to reduce sources of noise and envisions achieving order-of-magnitude sensitivity improvements in the near future.
This research is published in Physical Review D.
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is a Contributing Editor for Physics.