Dividing Work into Quantum Chunks
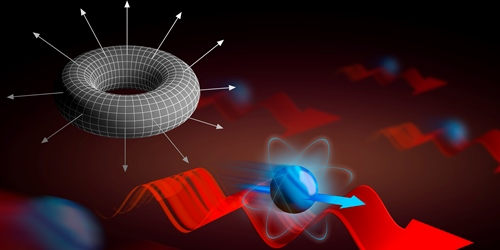
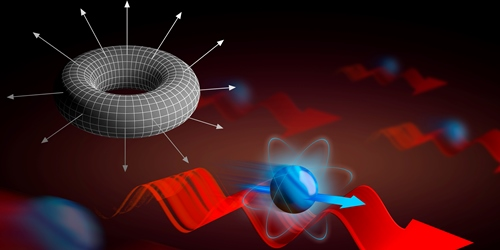
Work can be divided into smaller and smaller tasks without end, as typically there’s no quantum limit to how little work can be done. A new theoretical study, however, finds that this isn’t always the case. Bruno Mera of the Institute of Telecommunications in Lisbon, Portugal, and colleagues have shown that the work done on an atom by a complex electromagnetic field can take on discrete values when the system has certain “topological” features.
In most situations, work is not quantized. In the classic textbook example, the work required to move an object over some distance is equal to the applied force multiplied by the distance. Tweak the force slightly, and the work changes by a proportionately small amount—there are no discrete levels as found in, say, an atomic energy spectrum.
To see if work could be quantized, Mera and colleagues envisioned a system consisting of an atom confined to one dimension and interacting with an electromagnetic field coming from a light wave and an oscillating magnetic field. This combination acts like an electric field that pushes the atom a certain distance during each oscillation cycle. Because of the field’s periodic variation, the work done on the atom is “topologically protected,” a quantum effect that restricts certain quantities in a system to discrete values (see 7 October 2016 Focus story). As a result of this protection, the work value—which is an integer multiple of the Planck constant multiplied by the oscillation frequency of the magnetic field—is insensitive to tweaks to the magnetic field or other inputs. That robustness might open up future possibilities of storing information in the classical motion of atoms, say the authors.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Michael Schirber
Michael Schirber is a Corresponding Editor for Physics based in Lyon, France.