Neural Networks Know Their Knots
The use of neural networks in physics is booming. Recently, the tool has helped researchers uncover everything from new magnetic materials (see Synopsis: Discovering New Magnetic Materials with Machine Learning) to ways to reduce noise in electron beams produced at synchrotrons (see Synopsis: Noisy Synchrotron? Machine Learning has the Answer). Seeking their own neural network success, Liang Dai at City University of Hong Kong and colleagues wondered if the tool could classify knots, a computationally challenging problem. The team shows that the tool works, adding another win for this now ubiquitous method.
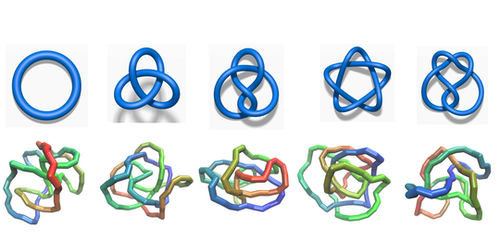
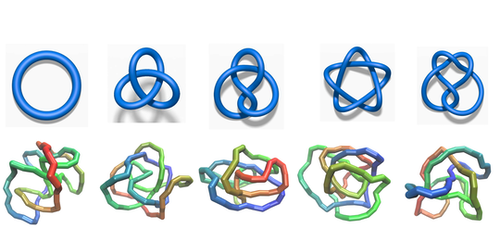
Earphone cables, shoelaces, and DNA are three of the myriad objects that can knot. A knot’s “type” is defined by the so-called knot invariant, a parameter linked to the knot’s topology. Many knots that look different actually have the same knot invariant value. This issue makes it tricky to judge whether two knots are topologically equivalent, and no practical method currently exists that can distinguish all knot types.
Dai and his colleagues applied two different neural networks to the problem—a recurrent neural network (RNN) and a feed-forward neural network (FFNN). An RNN can tackle problems that must be solved in a specific order. An FFNN can do the same but much less effectively. The team set the networks five different knots to classify. The RNN achieved 99% accuracy, while the FFNN correctly identified a knot only about 70% of the time. Dai was unsurprised by the result, noting that order matters for knots, as rearranging pieces of a knot can transform it into a different one.
This research is published in Physical Review E.
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is a Senior Editor for Physics.