Topology Inside a Liquid Crystal
The common vision of a liquid crystal is a fluid filled with hot-dog-shaped particles. The particles tend to align with each other, but regions of opposing alignment can meet at a discontinuous boundary. Now, Paul Monderkamp from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, Germany, and colleagues have classified these defects by assigning them a “topological charge” [1]. In simulations and experiments, the team found that the sum of these charges equals 1 for a variety of different container geometries (circle, triangle, square, etc.). This method of characterizing defects could apply to other systems, such as polycrystals and proteins.
Physicists are interested in the topology of defects in part because it offers a way to distinguish states in systems with competing constraints on their order. The orientational topology of liquid crystals had been studied before but only in nematic (unlayered) liquid crystals where the defects are points and are assigned charges of ±1∕2.
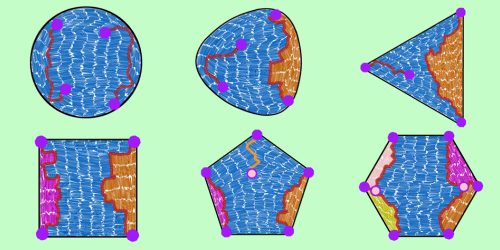
Monderkamp and colleagues have now investigated the topology of smectic (layered) liquid crystals in which the defects are a network of line boundaries. The team assigned a charge of ±1∕4 to the endpoints of each line boundary—the sign depending on how the particles changed orientation around the endpoint. In their simulations of a square box, for example, the particles near the top and bottom walls aligned horizontally, while those near the side walls aligned vertically. Separating these different regions were two boundaries, each having two endpoints with charge +1∕4. Other container shapes had similar charge arrangements—always summing to 1. The team verified their simulation results in experiments where rod-shaped colloids were allowed to settle at the bottom of a container.
–Michael Schirber
Michael Schirber is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Lyon, France.
References
- P. A. Monderkamp et al., “Topology of orientational defects in confined smectic liquid crystals,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 198001 (2021).