Three-In-One X-Ray Imaging
X-ray imaging is a powerful tool for monitoring the behavior of materials. For example, in 3D metal printing, scientists can use the technique to monitor the liquification of the metal powder, allowing them to better understand the behavior of the materials during the printing process. But so far, most x-ray analyses of metals in additive manufacturing have been limited in their scope, looking at one property—typically, attenuation—of the x-ray beam at a time. Now, Lorenzo Massimi at University College London and colleagues have devised a dynamical x-ray imaging method that simultaneously monitors three properties of the beam [1].
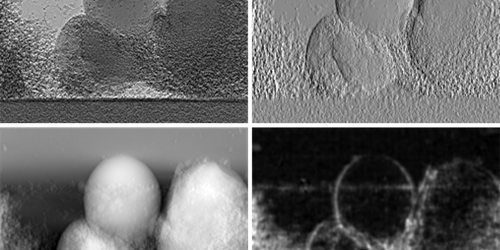
In their experiments, which were performed at the Diamond Light Source, UK, Massimi and colleagues shone an x-ray beam at a metal powder being melted by a laser. They placed a moving mask between the beam and the sample that split the beam into x-ray “beamlets.” They then used these beamlets to perform simultaneous measurements on the sample. In addition to attenuation, the researchers measured the phase shift of x rays transmitted by the sample, which allowed them to monitor changes in the density of the metal as it melted. They also measured the dark-field scattering of x rays by the sample, which allowed them to estimate the amount of molten powder.
From their images, the team observed that metal droplets began to form on the powder particles as the powder grew hotter. They were able to pinpoint where the droplets would form in the attenuation images prior to them appearing, thanks to subtle changes in the contrast of the phase and dark-field images. The properties of a metal when it is printed can make a huge difference in the final product’s quality, so understanding how the process plays out is key to improving the technique, the researchers say.
–Rahul Rao
Rahul Rao is a freelance science writer based in New York.
References
- L. Massimi et al., “Dynamic multicontrast x-ray imaging method applied to additive manufacturing,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 127, 215503 (2021).