Steering Light Within a Crystal
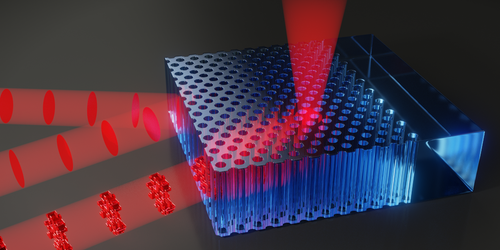
Ravitej Uppu has a conundrum—the best materials for housing qubits and certain other optically activated objects typically reflect incident light. By stopping externally applied light from reaching its target, this reflectivity presents a challenge for controlling optically integrated devices. Now, Uppu and colleagues at the University of Twente in the Netherlands have demonstrated a possible solution to this problem: a way of guiding light along an arbitrary path through a material by patterning the light’s phase [1]. Uppu says that the method, which the team applied to telecommunications-wavelength light, should work for light of any color, allowing the method to be used in devices ranging from chip-based lasers to quantum computers to photonic circuits.
In their demonstration, the Twente team shone an infrared beam into the edge of a 2D silicon crystal containing a periodic arrangement of air-filled pores. A large fraction of the light was reflected back along the beam, but because of disorder in the crystal, some was reflected out of the crystal at 90°. They captured this light with a camera.
The researchers steered the beam by iteratively modulating the phase of its wave front. Light detected by the camera indicated the beam’s target position in the sample; this information was then fed into an algorithm that predicted the phase pattern that, when applied to the beam, would allow the light to reach some other chosen position. After applying that phase pattern, they repeated the process to maneuver the light to the next position. The team now plans to build a 3D crystal and add additional cameras to steer light in higher-dimensional materials.
–Katherine Wright
Katherine Wright is the Deputy Editor of Physics Magazine.
References
- R. Uppu et al., “Spatially shaping waves to penetrate deep inside a forbidden gap,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 177402 (2021).