Inflating Muscles and Creeping Fingers Receive New Prize
Yesterday, the APS Division of Soft Matter announced the inaugural winners of the Gallery of Soft Matter video and poster contest (Fig. 1). Below are the winners.
Inflatable Muscles for Soft Robots
One day, while fabricating long, thin rods of a silicone elastomer, graduate student Trevor Jones says that he and his colleagues at Princeton University had “a happy accident.” While the elastomer was still liquid, air found its way into one of the molds. That air formed a bubble that rose to the top of the rod. When they removed the rod from the mold, they found that the bubble had hollowed part of it out, leaving in the rod a long, off-center cavity.
The team found that they could contort this partly hollow rod by injecting high-pressure air into the cavity. In subsequent experiments, they were able to engineer rods that performed specific sequences of complex deformations by “programming” into them different bubble geometries. This way, the team has created dynamic structures that can, for example, grip and then lift an object. Jones and his colleagues propose using their structures as actuators in soft robotics.
Creeping Fingers
“Experiment—where theory comes to DIE,” declares a sign on the door to the laboratory used by graduate student Savannah Gowen and her colleagues at the University of Chicago. Inside the lab, Gowen has conducted experiments which, although not the theory killer promised by the sign, have uncovered an interesting new phenomenon that the team had speculated might be seen.
When they made the discovery, Gowen and her colleagues were investigating the so-called Saffman–Taylor instability, an interfacial instability created when a less viscous fluid flows into a more viscous fluid. To create the instability, they confined a film of clear viscous fluid between two transparent plates. They then alternately injected dyed and undyed samples of a less viscous fluid. As the less viscous fluid spread, its leading edge formed finger-like protrusions—a long-observed pattern that gives the instability its alternative label of “viscous fingering”—while on the inside the alternating dyed and undyed samples formed outwardly moving concentric rings.
The Saffman–Taylor instability has been studied for decades, but, Gowen says, the team’s novel experiment allowed them to visualize the fluid flow in a new way. In particular, the concentric rings let them measure the flow velocity of the less viscous fluid far away from the interface, revealing a large-length-scale relationship between the flow velocity, the flow duration, and the geometry of the fingers.
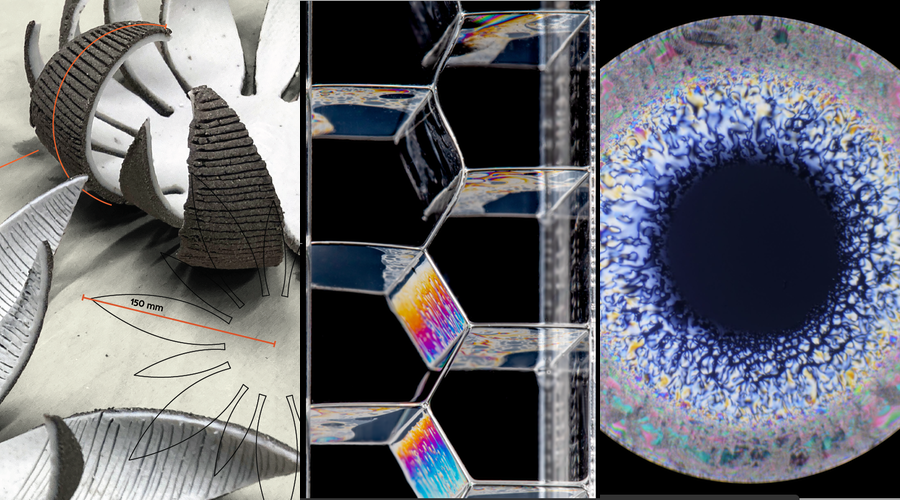
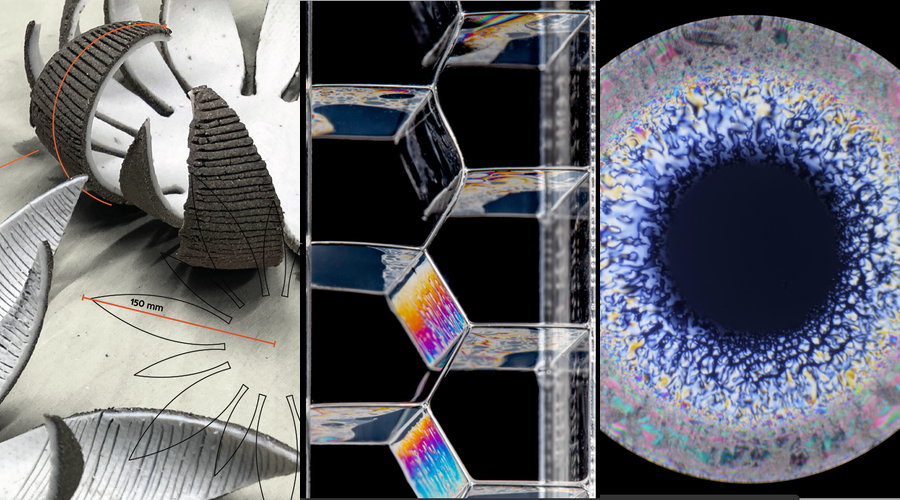
Ceramics, Liquid Crystals, and Bubbles
As well as the two videos, three posters received prizes. These posters show the effect of bubbles on the shape of an elastic ribbon; the release of “material frustration” in a structure made of two types of clay that shrink by different amounts when fired; and the structural phases that form in a liquid crystal drop as it evaporates.
–Marric Stephens
Marric Stephens is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Bristol, UK.