Quantum Thermal Transistor Amplifies Heat Currents
Like an electronic transistor controls electrical current in a circuit, a thermal transistor controls heat current, amplifying it or switching it between values. Macroscale thermal transistors are used to recycle waste heat in power systems; while microscale ones route heat away from delicate devices. In simple quantum systems, theoretical work shows that qubits interacting with thermal baths could perform the switching function of a thermal transistor. Now Nikhil Gupt and Arnab Ghosh of the Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur and their colleagues extend that work by proposing a quantum thermal transistor that can also amplify a heat current [1].
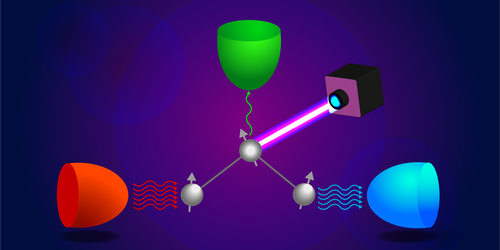
A typical quantum thermal transistor consists of three qubits coupled to three thermal baths. Varying the temperature of any one of these baths allows the corresponding coupled qubit to be used to control the heat current through the other two qubits. The transistor effect appears when the current in the former qubit is strong enough to switch the flow to the other two qubits.
Instead of varying the bath temperature, the researchers propose applying a repetitive force to one of the qubits using a pulsed laser. Their model shows that by doing so, researchers could use the excited qubit to control whether a current flows through the other two and to determine the amplitude of that current. Predictions indicate this design could increase current amplitude by a factor of 150 or more.
The researchers say that their solution, unlike previous proposals, will work even if the bath temperature approaches zero. It also avoids the energy-intensive step of changing bath temperature. The team says that their device could be realized using ultrathin-film qubits excited by a laser.
–Rachel Berkowitz
Rachel Berkowitz is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Vancouver, Canada.
References
- N. Gupt et al., “Floquet quantum thermal transistor,” Phys. Rev. E 106, 024110 (2022).