For the Love of Neutrinos
The team behind CUPID-0, a neutrino experiment that used a new type of precision heat detector, has released its final results [1]. The findings continue the ongoing particle-physics streak of not seeing neutrinoless double beta decays. These decays are at the heart of current neutrino research, as their detection would imply that neutrinos are their own antiparticle. CUPID-0’s nondetection improves—by a factor of 20—constraints from previous detectors using the same nuclear-decay target material.
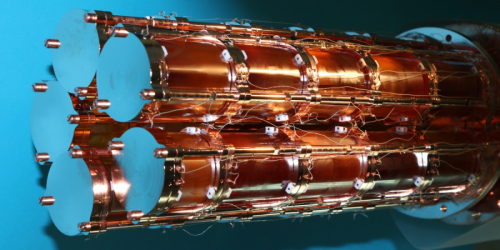
The CUPID-0 experiment, located at the National Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN) Gran Sasso National Laboratory in Italy, looked for neutrinoless double beta decays in selenium-82. This isotope is known to decay by “normal” double beta decay, in which two neutrons in its nucleus transform into two protons, emitting two electrons and two neutrinos in the process. The collaboration measured the spectrum of selenium-82 decays in crystal samples and looked for a peak that would signal decays without accompanying neutrinos.
For these measurements, the researchers used scintillating bolometers, a recently developed technology, combining heat sensors that can identify single decay events and light sensors that can discriminate beta decays from other types of nuclear decays.
Despite being about a tenth of the size of other detectors, the 10-kg CUPID-0 experiment achieved a relatively high measurement sensitivity. “This result opens the door for the CUPID-0 successor, CUPID, which will scale the technology to the level of a ton-scale detector,” says CUPID-0 team member Laura Cardani.
–Michael Schirber
Michael Schirber is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Lyon, France.
References
- O. Azzolini et al., “Final result on the neutrinoless double beta decay of 82Se with CUPID-0,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 129, 111801 (2022).