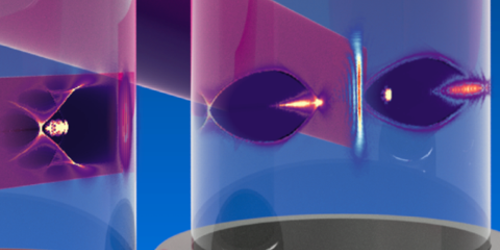
Two Plasma Accelerators Become One
Plasma acceleration is an emerging technique for the compact acceleration of charged particles. The technique can be used to accelerate particles to a speed close to that of light within just a few millimeters, a tiny fraction of the hundred or so meters required using a conventional particle accelerator. However, it is difficult to stabilize the energy and shape of electron beams produced using a plasma accelerator. Now Moritz Foerster of the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich and his colleagues show that they can create stable electron beams by combining two different plasma accelerators [1].
Researchers generally achieve plasma acceleration using one of two methods. In the first, known as laser wakefield acceleration, a laser is used to induce in a plasma moving waves of high and low electron density. The electric field of this wave pattern is strong enough that it can accelerate electrons to high energies. In the other method, known as plasma wakefield acceleration, a beam of charged particles is used to create the density waves. This method produces a denser and more stable electron beam, but it requires a particle accelerator to create the particle beam used to induce the waves.
Foerster and his colleagues combined the two methods, harnessing the compactness of the laser-driven method with the beam quality of the particle-driven one. Using the laser method, they produced a fast but relatively messy electron beam. This beam was then used as the input for the particle-driven method, which produced a denser, more stable beam. The team are working on further improving the electron-beam quality, such that it has the stability level needed to drive a compact x-ray free electron laser.
–Sophia Chen
Sophia Chen is a freelance science writer based in Columbus, Ohio.
References
- F. M. Foerster et al., “Stable and high-quality electron beams from staged laser and plasma wakefield accelerators,” Phys. Rev. X 12, 041016 (2022).