Informing Potential Remedies for Quasiparticle Poisoning
Over the past few decades, superconducting circuits have emerged as a promising technology, with applications from quantum information processing to quantum sensing. Operated within cryostats in the 10 mK range—roughly 100 times colder than outer space—these devices rely on conduction electrons coalescing into a superconducting condensate such that they flow as one entity. However, historically, these superconducting circuits have been plagued by electronic excitations known as Bogoliubov quasiparticles with populations much larger than would be expected given the cryostat temperature (Fig. 1) [1]. This so-called quasiparticle poisoning can cause decoherence of quantum information in superconducting circuits. Now an experiment by Thomas Connolly and Pavel Kurilovich of Yale University and colleagues reveals new insights into this phenomenon [2]. The results suggest that poisoning can be mitigated by engineering the energy landscape over which these quasiparticles move.
Quasiparticles result from the splitting of Cooper pairs—the coupled electrons that carry charge inside a typical superconductor. This splitting occurs when a pair is excited with an energy called the gap energy, which depends on the type of superconducting material used. For an aluminum superconductor (as used in the current study), the gap energy is around 180 µeV, which corresponds to a critical temperature of about 1 K. When a superconductor is cooled below the critical temperature, we would expect that the number of quasiparticles would be very small, just based on thermodynamics. But the number density is many orders of magnitude higher than expected.
For decades, researchers have struggled to explain this quasiparticle puzzle. Over the past five years, however, two major sources of quasiparticles have been carefully characterized in the context of quantum information processing applications. The first is photon-assisted tunneling across a Josephson junction, which is a barrier between two superconductors. Quasiparticles can be created at such a junction when an infrared photon from the environment splits a Cooper pair across the junction [3]. The second source is ionizing radiation, such as cosmic-ray muons and gamma rays [4]. When these particles impact the device substrate, they create a shower of phonons that can lead to quasiparticle creation in the superconductors. These phonon bursts are particularly problematic for quantum error correction, as the generated quasiparticles can simultaneously cause errors in multiple superconducting qubits on the same substrate [5].
To better understand quasiparticles and how their associated errors might be reduced, Connolly and colleagues investigate quasiparticle dynamics in a transmon qubit, the most widely used superconducting qubit today. This simple superconducting circuit is an anharmonic oscillator consisting of a Josephson junction shunted by a capacitor. As is often done in quasiparticle studies, Connolly and colleagues designed their transmon to be sensitive to changes in the capacitor’s charge [6]. In this regime, the researchers could monitor the qubit frequency in real time and attribute frequency jumps to the tunneling of a single quasiparticle across the Josephson junction.
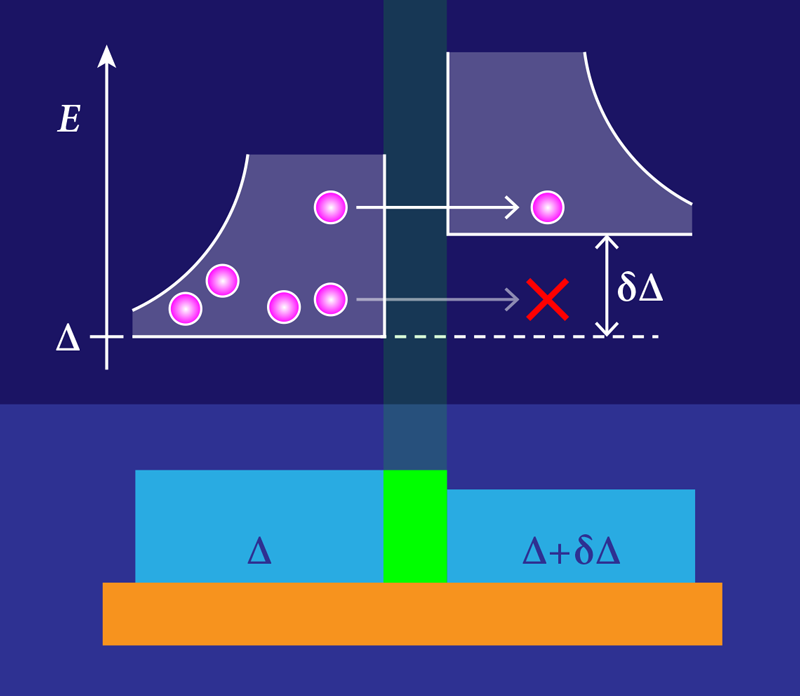
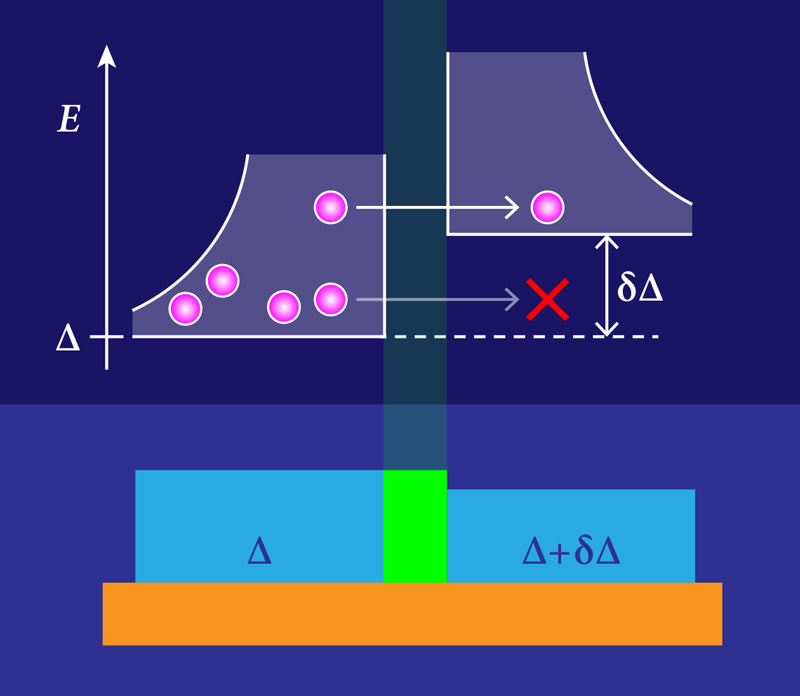
Normally, the tunneling events across a Josephson junction can be attributed to preexisting quasiparticles diffusing through the circuit, or they can be from the aforementioned photon-assisted tunneling process. To suppress the latter, Connolly and colleagues used strong infrared filtering on the device control lines [7] and light-tight shielding [8]. This setup let them focus on the remaining quasiparticle density in a way that was difficult in previous experiments. The Josephson junction in the team’s transmon consisted of two films of aluminum separated by an oxide layer. One of the films was slightly thinner than the other, giving it a slightly larger gap energy. The team monitored the quasiparticle tunneling rate across this junction as the temperature of the cryostat was increased, revealing information about the energy distribution of the quasiparticles.
In particular, the researchers observed that the tunneling rate increased as they raised the base cryostat temperature above 20 mK, finding that the rate increase was well described by a thermal activation model. This model assumes that the quasiparticles have a thermal energy distribution and that tunneling only occurs for those quasiparticles with energy greater than the difference in the gap energies between the two films. From the model, the temperature of the quasiparticles was found to be the same as that of the cryostat, suggesting that quasiparticle energies rapidly thermalize with their cold environment—despite their number density being much higher than equilibrium.
Connolly and colleagues bolstered this picture by measuring the quasiparticle tunneling rate when the transmon qubit was both in its ground state and in its excited state. The tunneling rate went up faster with temperature when the qubit was in the excited state, which can be attributed to the quasiparticles stealing energy from the qubit. (This energy stealing is the main source of quasiparticle-induced decoherence in superconducting qubits [9]). All their observations taken together imply that—at cold temperatures—the quasiparticles primarily reside in the lower gap film. As temperatures approached ∼100 mK, they observed an increase in the tunneling rate consistent with the creation of new quasiparticles—that is, the initial onset of temperature-induced breakdown of superconductivity throughout the device. At these higher temperatures, both the number of quasiparticles and their energy distribution were well described by the cryostat temperature.
The observation that the quasiparticles are all individually well thermalized with the cryostat temperature—despite their nonequilibrium population—is important for efforts to mitigate the impact of ionizing radiation. A leading strategy to fight these radiation-induced quasiparticle bursts is “gap engineering,” where the spatial profile of the superconducting gap energy is modulated to keep quasiparticles away from sensitive regions of the device [10]. But this only works if quasiparticles have “cold”-energy distributions and can be corralled in low-energy landscapes. Previous work suggested that this is the case, but Connolly and colleagues have provided direct evidence that quasiparticles on average relax to the lowest energy state in their neighborhood. However, because radiation-induced bursts represent a significant increase in the number of quasiparticles on rapid (roughly microsecond) timescales, an open question remains: How quickly after an impact do quasiparticles thermalize with the cryostat? While some experiments suggest it is “fast enough” for the success of gap engineering, only more careful investigation will tell us for sure.
References
- J. Aumentado et al., “Quasiparticle poisoning in superconducting quantum computers,” Phys. Today 76, 34 (2023).
- T. Connolly et al., “Coexistence of nonequilibrium density and equilibrium energy distribution of quasiparticles in a superconducting qubit,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 217001 (2024).
- M. Houzet et al., “Photon-assisted charge-parity jumps in a superconducting qubit,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 123, 107704 (2019).
- A. P. Vepsäläinen et al., “Impact of ionizing radiation on superconducting qubit coherence,” Nature 584, 551 (2020).
- C. D. Wilen et al., “Correlated charge noise and relaxation errors in superconducting qubits,” Nature 594, 369 (2021).
- D. Ristè et al., “Millisecond charge-parity fluctuations and induced decoherence in a superconducting transmon qubit,” Nat. Commun. 4, 1913 (2013).
- M. Halpern et al., “Far infrared transmission of dielectrics at cryogenic and room temperatures: glass, Fluorogold, Eccosorb, Stycast, and various plastics,” Appl. Opt. 25, 565 (1986).
- R. Barends et al., “Minimizing quasiparticle generation from stray infrared light in superconducting quantum circuits,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 99 (2011).
- G. Catelani et al., “Relaxation and frequency shifts induced by quasiparticles in superconducting qubits,” Phys. Rev. B 84, 064517 (2011).
- S. Diamond et al., “Distinguishing parity-switching mechanisms in a superconducting qubit,” PRX Quantum 3, 040304 (2022); M. McEwen et al., “Resisting high-energy impact events through gap engineering in superconducting qubit arrays,” (2004) arXiv:2402.15644.