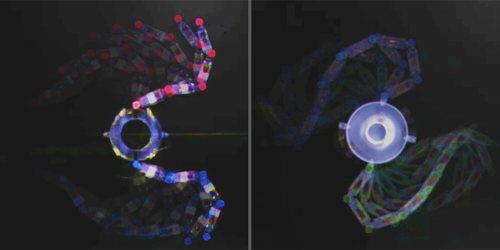
Toy Robots Mimic Swimming Algae
The freshwater alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii swims by flapping its two cilia in a motion akin to the breaststroke. Unlike a human, C. reinhardtii lacks a brain to coordinate its limbs. The synchronization is automatic. To uncover its origin, Mingcheng Yang of the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and his collaborators built mechanical algae whose cilia are made of chains of cockroach-sized toy robots [1]. By adjusting the cilia’s flapping frequency and other parameters, the researchers reproduced the alga’s swimming gaits and identified the conditions that favor them.
Yang’s mechanical algae each consists of a puck-like base, on the sides of which are attached two chains of four robots. Each robot’s underside bristles with elastic hairs set at an angle. When a mechanical alga is placed on a tabletop and an internal electric motor is switched on, each bristly robot vibrates vertically. On the upstroke, the hairs push the robot toward the base, setting up the possibility that the chains could buckle.
The voltage applied to the robots’ motors, which control the frequency at which the robots vibrate, determines whether the buckling is periodic. Friction between the base and the table determines whether the two chains synchronize. The weaker the friction, the greater the chains’ ability to influence each other’s motion.
Yang and his colleagues adjusted the two chains’ frequencies, the base’s friction, and other parameters and recorded video of the variety of motions that resulted. Among them were the in-phase breaststroke of wild-type C. reinhardtii and an antiphase stroke—which doesn’t provide effective motion—seen in mutant C. reinhardtii. A model developed by the researchers matched their observations and revealed that the stable swimming gait corresponds to maximum energy dissipation, a result that the researchers say is both a surprise and a puzzle.
–Charles Day
Charles Day is a Senior Editor for Physics Magazine.
References
- Y. Xia et al., “Biomimetic synchronization in biciliated robots,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 133, 048302 (2024).