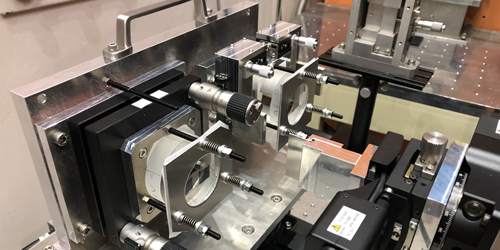
Searching for New Physics in the Neutron Looking Glass
Some theories of beyond-standard-model physics predict that neutrons passing close to an atomic nucleus will experience exotic interactions with the particles in that nucleus. To try to spot these interactions, physicists use a neutron interferometer, a device that splits and then recombines a neutron beam. If a currently unknown particle interaction affects one branch of the split beam as it passes through a material, the signature should show up in the interference pattern that forms when the two beams come back together. Takuhiro Fujiie at Nagoya University, Japan, and colleagues have now demonstrated a new neutron interferometer that promises greater sensitivity to beyond-standard-model physics [1].
In a conventional neutron interferometer, components made of crystalline silicon manipulate the neutron beam. Such interferometers only work for neutron beams that have wavelengths between 0.19 and 0.44 nm because of the spacings between crystalline silicon’s atoms. In the new instrument, neutron mirrors composed of alternating layers of nickel and titanium manipulate the neutron beam. The spacing of the layers determines the wavelength reflected and can be tuned to make mirrors that work for a wider range of neutron-beam wavelengths—including longer wavelengths that offer greater measurement sensitivity.
To test their device, Fujiie and his team took advantage of the bright, short-duration neutron pulses generated at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. Compared to interferometry experiments that use continuous beams, experiments using pulsed beams are less affected by measurement drift over time, reducing error. Fujiie says that the tests, which involved passing one branch of the split beam through a silicon, an aluminum, or a titanium target, were “only a very brief demonstration.” Nevertheless, the initial results are comparable to those obtained with a conventional device.
–Marric Stephens
Marric Stephens is a Corresponding Editor for Physics Magazine based in Bristol, UK.
References
- T. Fujiie et al., “Development of neutron interferometer using multilayer mirrors and measurements of neutron-nuclear scattering length with pulsed neutron source,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 023402 (2024).