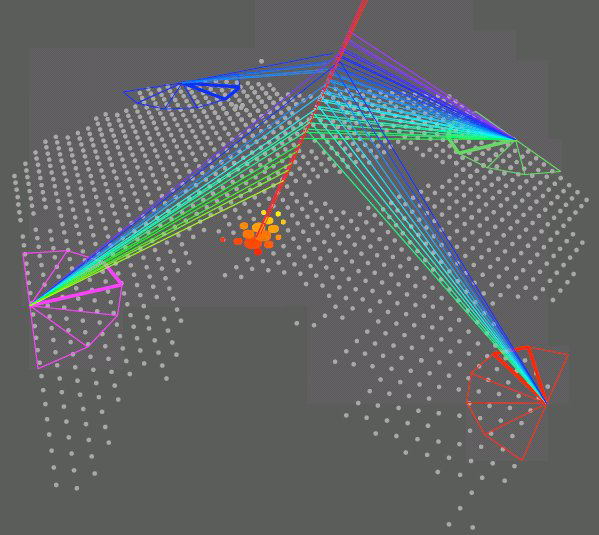
Air showers from ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays
The nature and origin of ultrahigh-energy ( >1018eV) cosmic rays remain a mystery. Astrophysicists hunt for clues regarding their mass composition, which, along with other properties such as the flux and arrival direction distribution, should help distinguish among the various models of the sources and propagation of cosmic rays. However, because of the low flux of ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays, the mass composition cannot be measured directly. Instead, it is inferred from measurements of the extensive air showers—the cascades of high-energy ions created when incident cosmic rays collide with atoms in the atmosphere. The atmospheric depth at which development of a shower reaches its maximum number of secondary particles depends on the mass and energy of the incident particle. Data on the depth of the maximum thus provide information about the mass composition.
The Pierre Auger Collaboration has presented in Physical Review Letters new measurements of extensive air showers from ultrahigh-energy cosmic rays. Their observations suggest a gradual increase in the average mass of cosmic rays in a region of energies around 1019eV. The data are the highest statistics measurements to date. – Stanley Brown