Perhaps no “bump” in the data
An unexpected finding in a particle physics experiment must be reproduced to rule out the possibility that it is only a statistical fluctuation or due to something other than new physics. This is a primary reason for having more than one experiment studying the same kind of signal at a high-energy particle collider. At Fermilab, there are two such experiments: CDF and D0.
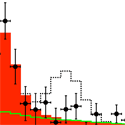
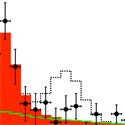
In April 2011, the CDF collaboration reported a standard deviation excess in the number of events with a boson and a pair of jets whose invariant mass was in the – giga-electron-volt ( ) range (see T. Aaltonen et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 171801). One possible explanation for that excess was an unexpected new particle, with a cross section of approximately picobarn ( ). Now, the D0 collaboration reports in Physical Review Letters their analysis of the same type of events. They see no evidence for such an excess, ruling out a particle with a cross section at the standard deviation level.
The two Fermilab experiments appear to disagree, but it’s not yet clear why. To facilitate comparison between the results, D0 made their search parallel to the CDF search to a good approximation, but there were small differences in how the two collaborations handled systematic errors, and of course the detectors are different.
It is also possible that CDF saw an upward fluctuation in the production of some new particle while D0 saw a downward fluctuation. D0 addresses this possibility, showing their values for a range of potential signal cross sections. For example, there is only a chance that a particle with a cross section is compatible with D0’s data. Further results are needed to clarify the situation. – Robert Garisto