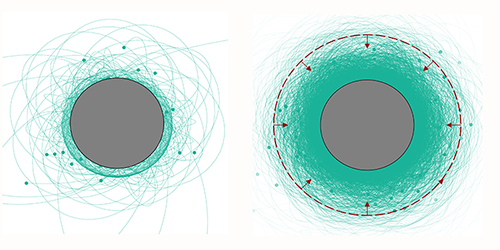
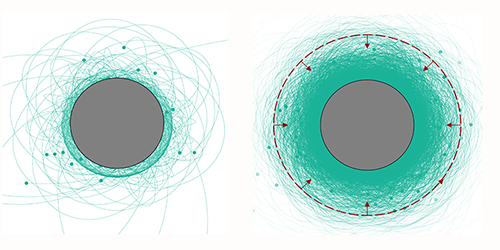
Axion Clouds Enveloping Pulsars
Theorized lightweight particles called axions could solve two major open problems in physics: the identity of dark matter and the strong nuclear force’s puzzling respect of so-called charge–parity symmetry. The quest to detect the putative particles, both in the lab and in the cosmos, often relies on their behavior in strong magnetic fields. Like previous investigators, Dion Noordhuis of the University of Amsterdam and his collaborators propose looking for axions in the intense magnetic fields of rapidly rotating neutron stars called pulsars. Their new insight is that those axions, trapped by the pulsar’s gravitational field, could pile up to form a dense cloud that could imprint a detectable signature on the pulsar’s radio spectrum [1].
The axion’s mass is weakly constrained by theory and observation. Noordhuis and collaborators calculated that axions within a broad mass range (between 10–9 and 10–4 eV) will unavoidably become gravitationally trapped around pulsars. Thanks to their feeble interactions with photons and other particles, the axions would survive for the lifetime of the pulsar—millions of years—enough for a thick cloud to accumulate around the pulsar. The size and density of such a cloud could be sufficient for weak interactions involving axions to produce sizeable signals. In particular, the axions’ coupling to photons would produce a narrow line in the pulsar spectrum at a frequency related to the axion mass—a signature that would be in contrast with the typically smooth spectrum observed from pulsars. Noordhuis and his collaborators say that, once they have refined their calculations, they could use radio data to search for these narrow spectral lines. Moreover, if such a line is not seen, this nondetection would yield the most stringent limit yet on the axion’s coupling to photons.
–Charles Day
Charles Day is a Senior Editor for Physics Magazine.
References
- D. Noordhuis et al., “Axion clouds around neutron stars,” Phys. Rev. X 14, 041015 (2024).