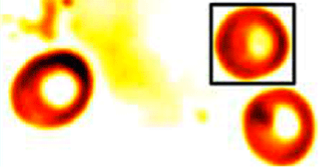
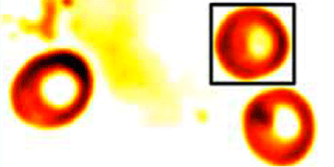
How Much Does a Cell Weigh?
If you had to estimate the mass of the average human cell, you could cheat and look it up on Wikipedia, or do a back-of-the-envelope calculation with a few assumptions about the mass and volume of a person (a cylinder) and the size of cells (spheres). But researchers need more precise measures of a cell’s mass so they can detect small changes as it grows or responds to its environment. In Physical Review Letters, Kevin Phillips and colleagues at the Oregon Health & Science University in Portland report a simple way to measure the mass of individual red blood cells with a commercial microscope.
To do this, Phillips et al. have developed a technique called tomographic bright-field imaging, which reconstructs the 3D optical index of refraction of a microscopic object, like a cell or plastic bead, and then converts this information into the object’s mass. The team places a narrow aperture in front of a microscope light source to make a unidirectional plane wave and passes this light through a glass slide containing red blood cells. A CCD camera on the opposite side of the slide maps out the light intensity. Phillips et al. feed a series of these intensity maps, each corresponding to the slide at different distances from the focal point of the light source, into a numerical model that reconstructs the 3D index of refraction of the cells. They then use tabulated values to relate the index to the mass density of the red blood cells (and some other tricks to find their volumes), arriving at a mass of roughly 27 picograms (1 picogram =10-12 gram) per cell.
Measuring cell masses optically is less destructive than other methods and could, according to the authors, be incorporated into lab-on-a-chip studies of bacteria, human cell lines, and patient samples. – Jessica Thomas