Tiny Tractor Beam
Since the 1980s, scientists have been grabbing and tugging tiny particles over microscopic distances with “optical tweezers,” for example to probe the mechanical responses of biomolecules. Now in Physical Review Letters, David Ruffner and David Grier of New York University describe pushing and pulling particles over relatively long distances—tens of microns and, in principle, much longer—using a “tractor beam” that could prove more versatile.
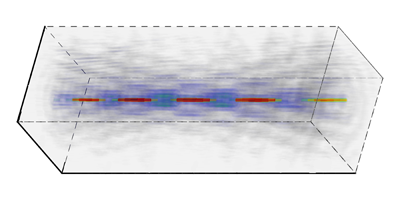
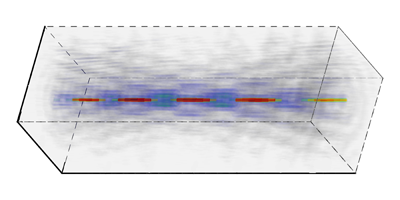
A true tractor beam comes from only one direction. For a particle to be pulled rather than pushed, it must redirect the momentum of enough photons “downstream” to overcome the force of the photons hitting it from upstream. This can happen if the intensity of light changes rapidly along the axis of the beam, for example, where it is tightly focused.
To create intensity changes over a larger region, Ruffner and Grier exploited the carefully shaped light known as a Bessel beam, which travels without spreading. To approximate such a beam, they shined a laser on a device that let them electronically alter the phase in a circular ring, and then focused the light with a lens. A second, larger ring formed another beam that interfered with the first along the axis, forming an extended, moving array of light and dark regions that can capture and transport different types of particle. By adding another tractor beam, the researchers simultaneously pulled one particle while they pushed another nearby.
Although the technique won’t be snagging enemy spacecraft anytime soon, it could be a powerful way to manipulate objects under a microscope. – Don Monroe