Seeing the Glass of Milk as All Empty
A glass of milk is opaque because light scatters off of randomly placed molecules. But disordered materials like milk or clouds could appear transparent to certain combinations of waves that constructively interfere with each other. Previous experiments have realized enhanced transmission, but now, for the first time, researchers have observed transmission (as well as reflection) of acoustic waves traveling through a two-dimensional disordered medium.
A disordered material presents incoming waves with a random field of scatterers. A single plane wave could never wind its way through this thicket, but several plane waves coming in at different directions could scatter in a constructive way. Theorists predicted years ago that certain wave combinations could produce full transmission or reflection, but identifying these so-called “open” or “closed” channels is challenging because most systems have an enormous set of possible incoming waves.
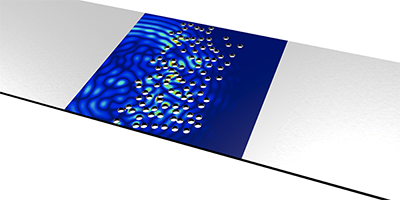
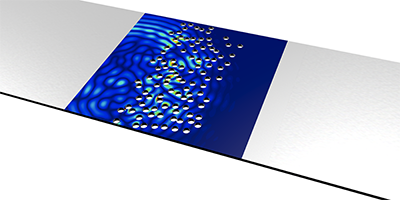
To reduce the size of the problem, Alexandre Aubry and his colleagues from the Langevin Institute (ESPCI ParisTech, CNRS) in France looked at acoustic (vibrational) waves traveling on an aluminum plate with randomly drilled holes that act as scattering sites. Laser pulses generated incoming waves at separate points on the plate, and the resulting vibrations were recorded at specific output points. From this data, the researchers derived an input-output transmission matrix, which allowed them to compute the combination of input waves corresponding to open (closed) channels. They subsequently prepared such waves and verified that their transmission (reflection) was roughly . The results provide the first demonstration of long-standing theoretical predictions and might help design optimal schemes for controlling wave propagation in digital communication channels.
This research is published in Physical Review Letters.
–Michael Schirber