Semiconductor Lasers Get Nervy
The brain’s information processing ability has inspired researchers to build neuromimetic computing systems from building blocks that behave like neurons. To accurately mimic neural behavior, these individual units should exhibit the characteristic of so-called excitable media, like axons—appendages that transmit impulses away from the body of neuron cells: Axons respond to a stimulus below a threshold with small, linear responses; above threshold, they respond with a large nonlinear response. Essential to their operation is a refractory period following the nonlinear events, during which any response is temporarily inhibited.
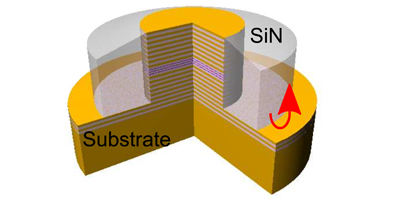
In a paper in Physical Review Letters, Sylvain Barbay and colleagues at the CNRS Laboratoire de Photonique et de Nanostructures in France, demonstrate that semiconductor lasers can reproduce the refractory period of an excitable system and thus could form the basis of optical computing architectures. The researchers studied the response of a micropillar laser with an intracavity saturable absorber (a material that blocks low-intensity light but allows high-intensity light through). The micropillar laser is pumped continuously just below threshold while another laser provides pulses that push the excitation above threshold. The response stimulated by such pulses is measured via the microlaser emission.
By using pairs of pump pulses with varying delay, the researchers were able to map out the refractory period, which consists of an “absolute” portion for delays less than picoseconds (no response at all to the pump pulse) and a “relative” portion between and picoseconds (the response begins to recover). The confirmation that the micropillar laser with saturable absorber is an excitable system with an absolute and relative refractory period may lead to its use in a variety of optical neural networks. – David Voss