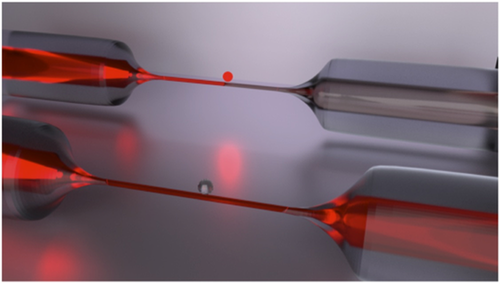
Diode for Single Photons
A “light diode” that passes photons in only one direction would be an essential element in nanoscale integrated optical circuits. Now a research team has built a prototype of such a device that works even for single photons. Light traveling through an optical nanofiber in one direction is mostly absorbed by atoms trapped just outside the fiber, while light traveling in the reverse direction can pass freely.
Light-based circuits could potentially send data faster and with lower power consumption than electronic circuits. To realize such schemes, optical engineers will need many of the same device types found in electronic circuits, such as diodes and transistors. Optical diodes, which allow light to travel in one direction but not the other, exist already, but they can't work with the low-intensity light signals, down to just a few photons, that optical circuits will require.
In previous experiments, a team at the Vienna University of Technology led by Arno Rauschenbeutel aimed a laser at a scattering object—a metal nanoparticle or a small cloud of cold atoms—trapped next to the middle of a narrow optical fiber. The scattered light entered the fiber, and the direction it traveled was under the team's control, based on their choice of the polarization of the incoming light [1, 2]. This trick exploited a surprising property of light traveling through a nanofiber narrower than the light's wavelength: the light can develop a spin that points perpendicular to the propagation direction. This means that the electric field vector rotates around an axis that is perpendicular to the direction the light travels through the fiber, unlike typical circularly polarized light, where the axis is parallel to the propagation direction. Reversing the direction of travel reverses the photons’ spin. The electric field extends some distance beyond the fiber surface and interacts with the scattering object just outside.
Now Rauschenbeutel and colleagues have reconfigured their earlier cold atom experiment to create a diode. In their new experiment, linearly polarized photons entered an optical fiber at one end before it tapered to a narrow “waist” 500 nanometers in diameter. The researchers held cesium atoms, cooled to about 30 microkelvin, in a linear array about 230 nanometers from the fiber. The atoms’ spins were aligned by a separate laser pulse, and the light frequency in the fiber was selected to correspond to that of an electronic transition of the atoms. With this matched frequency, the atoms could, in principle, absorb each photon that came through the fiber by interacting via the electric field that extends beyond the fiber surface. But absorption only occurs for a particular relative orientation of the photon spin and the atomic spin—that is, for photons traveling in one direction but not the other.
For the cesium atom array, the distance between the atoms and the fiber resulted in a relatively weak interaction of each atom with the photons. Around 27 atoms in the trap were, however, enough to produce a large ratio of forward to reverse transmission. In a second experiment, Rauschenbeutel and colleagues performed the same measurement for a single rubidium atom. They used a so-called microresonator (a tiny glass cylinder in which the light propagates around the circumference in a loop) to allow the same photons to interact many times with the atom and thus to boost the strength of the coupling. With the two experiments, “we demonstrated that our concept is general: it can be implemented in all coupling regimes from weak to strong,” says Vienna team member Jürgen Volz. This is important, he says, because a more practical version of the scheme that replaces the atoms with something easier to work with might only be able to access one regime or the other.
While the experiments demonstrate a proof of principle, a practical device for use in photonic circuits would need to replace the trapped atoms with some kind of solid-state structure, says Vahid Sandoghdar of the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light in Erlangen, Germany. Possibilities do exist for that, say the Vienna team, such as isolated dopant atoms or other defects in a solid material.
This research is published in Physical Review X.
–Philip Ball
Philip Ball is a freelance science writer in London. His latest book is How Life Works (Picador, 2024).
References
- R. Mitsch, C. Sayrin, B. Albrecht, P. Schneeweiss, and A. Rauschenbeutel, “Quantum State-Controlled Directional Spontaneous Emission of Photons into a Nanophotonic Waveguide,” Nature Commun. 5, 5713 (2014).
- J. Petersen, J. Volz, and A. Rauschenbeutel, “Chiral Nanophotonic Waveguide Interface Based on Spin-Orbit Interaction of Light,” Science 346, 67 (2014).